Figure 4.
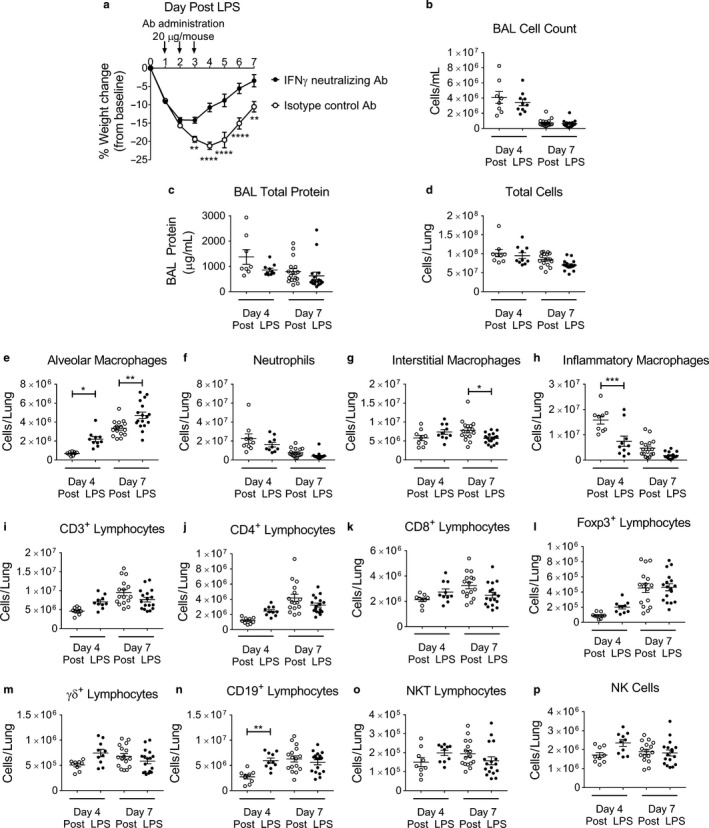
Interferon‐γ neutralization augments ALI recovery. WT mice were challenged with LPS administered at day 0 and then on days 1, 2, and 3 post LPS mice were given intraperitoneal injections of 20 μg/mouse of either an IFN‐γ neutralizing antibody or isotype control antibody. Mice were weighed daily and examined at day 4 or 7 post LPS for injury parameters or immunophenotyping in the BAL compartment or lung digests (n = 8–17 per group, combined from at least two independent experiments) (a) Body weight relative to baseline determined after injury. (b) BAL cell counts numbers total protein concentration, (c) BAL total protein concentration, and (d) Total lung cell counts obtained from enzymatically digested single‐cell suspension are similar between antibody administrations. (e–h) Changes in lung macrophage subpopulations and neutrophils as total numbers in single‐cell suspensions determined by flow cytometry with gating adapted from Misharin et al. (2013). (i–p) Changes in CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, Foxp3+, γδ+, CD19+, NK T lymphocytes subsets and NK cells as total numbers in single‐cell suspensions determined using a previously published lymphocyte flow cytometric panel and gating approach (Mock et al., 2019). p values determined by two‐way ANOVA with the Holm–Sidak multiple comparison tests. *p < .05, **p < .01 ***p < .001, ****p < .0001
