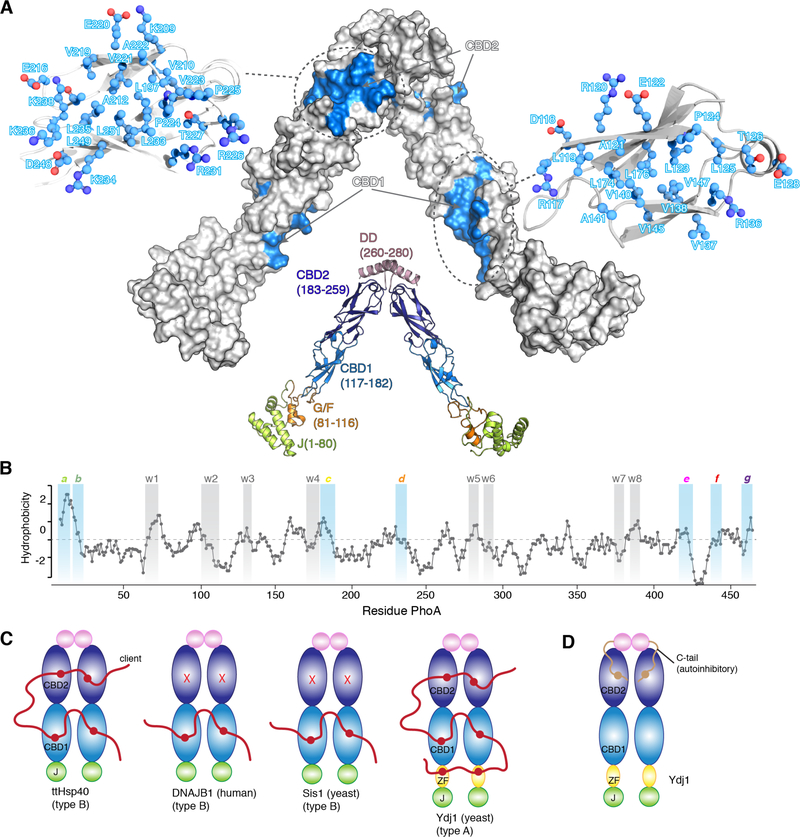
Fig. 1. Interaction between Hsp40s and client proteins.
(A) The structure of ttHsp40 is shown in cartoon and the various domains, with their amino acid residue boundaries, are labeled. The client-binding sites are colored blue on a solvent-exposed surface model of ttHsp40. The residues that make up the client-binding sites are shown in ball-and-stick. (B) Hydrophobicity plot of PhoA as a function of its primary sequence. A hydrophobicity score (Roseman algorithm, window = 9) higher than zero denotes increased hydrophobicity. The sites identified by NMR to be recognized by ttHsp40 are highlighted in blue (strong) or grey (weak). The strong sites are labeled a through g and the weak sites are labelled w1 through w8. (C) Domains involved in client binding in various Hsp40s as determined by NMR. ZF denotes the zinc finger domain in Ydj1. (D) The identified auto-inhibitory mechanism in Ydj1 mediated by the interaction of its C-tail and CBD2.