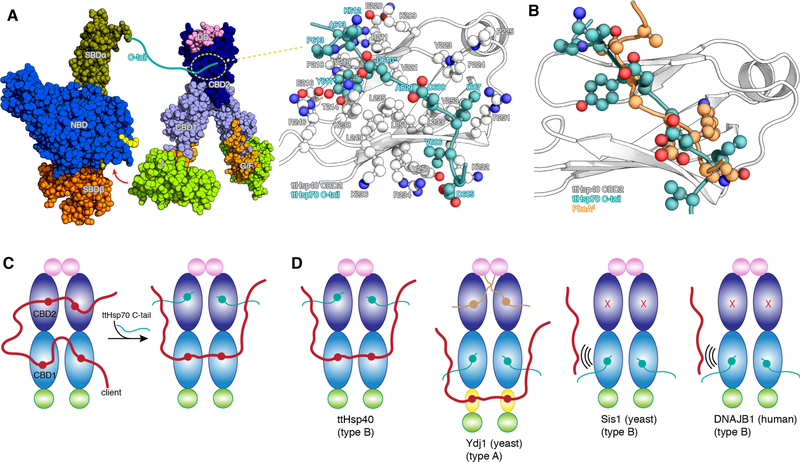
Fig. 3. Interaction between ttHsp70 and ttHsp40.
(A) Hsp70 (PDB ID 5NRO) and ttHsp40 shown as space-filling models. The red arrow indicates the interaction between the J domain and the NBD of Hsp70 as observed by NMR and crystallography (35). The ttHsp70 C-tail interacts with CBD2 of ttHsp40 and the NMR structure of their complex is shown in the expanded view. D610 and Y611 in ttHsp70 C-tail are the most important residues for mediating its interaction with ttHsp40 CBD2. (B) Overlay of the structures of the ttHsp70 C-tail and PhoAd, both in complex with ttHsp40 CBD2, shows that their binding to CBD2 is mutually exclusive. (C) Schematic of ttHsp40 showing the competition between the client and Hsp70 C-tail for CBD2. (D) Summary of the present NMR findings on the competition between client and Hsp70 C-tail in various Hsp40s. Sis1 and DNAJB1 use only CBD1 to interact with either the client or Hsp70 and cannot engage simultaneously both partners.