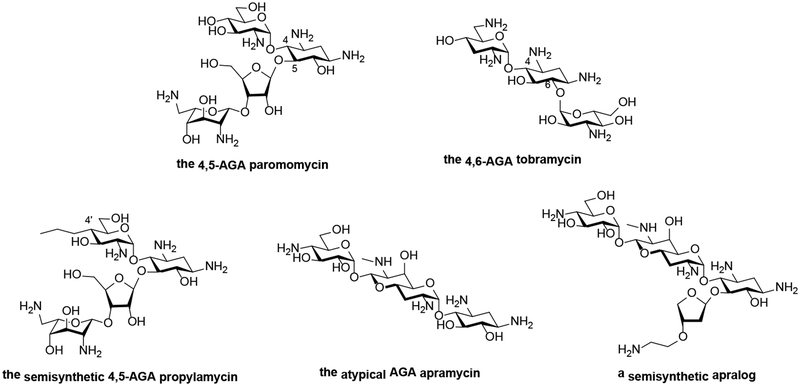
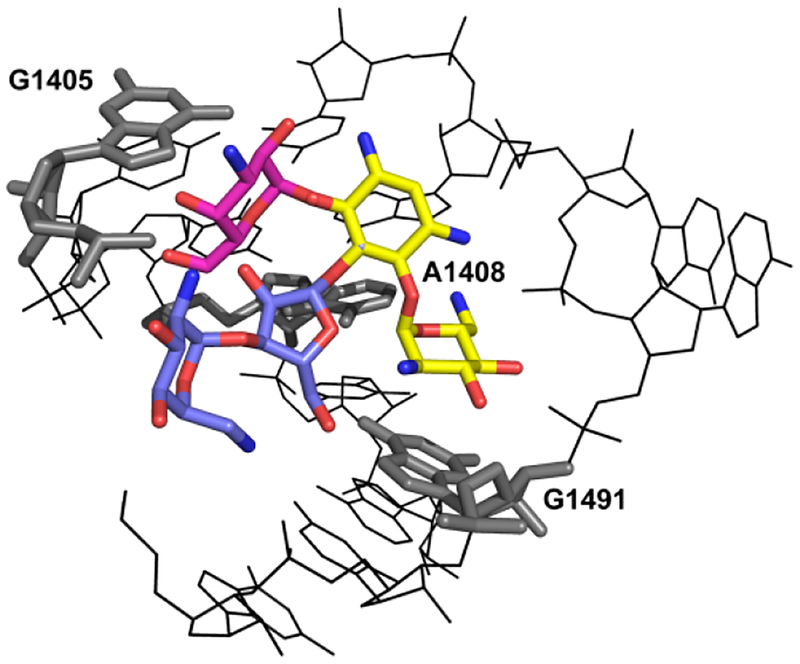
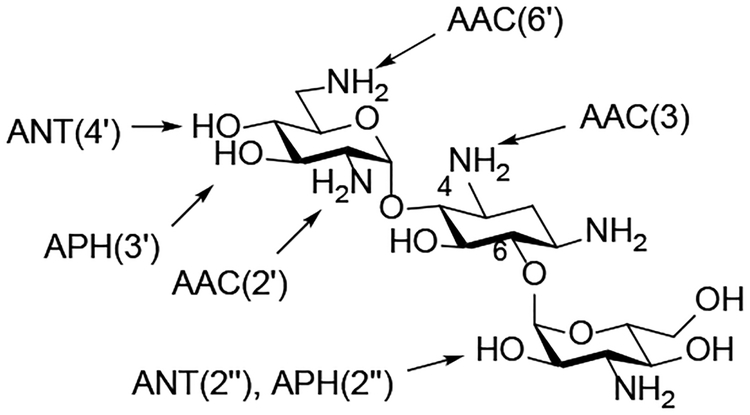
Figure 1.
A Chemical structures of 4,5-, and 4,6-aminoglycosides, of propylamycin, apramycin, and an apralog.
B View of the three-dimensional structure of the A-site loop within rRNA helix 44, the drug binding pocket, complexed with 4,5- and 4,5-disubstituted AGAs: the common neamine core is denoted in yellow; ring III of the 4,6-compounds (kanamycin) is denoted in red; rings III and IV of the 4,5-compounds (paromomycin) are denoted in blue. Indicated are the polymorphic residues (1408, 1491) and G1405, the target for methylation by RMTases.
C AMEs Acting on the 4,6-AGA Kanamycin B