Fig. 9: ER channels contributing to Ca2+ release in ICC-SS.
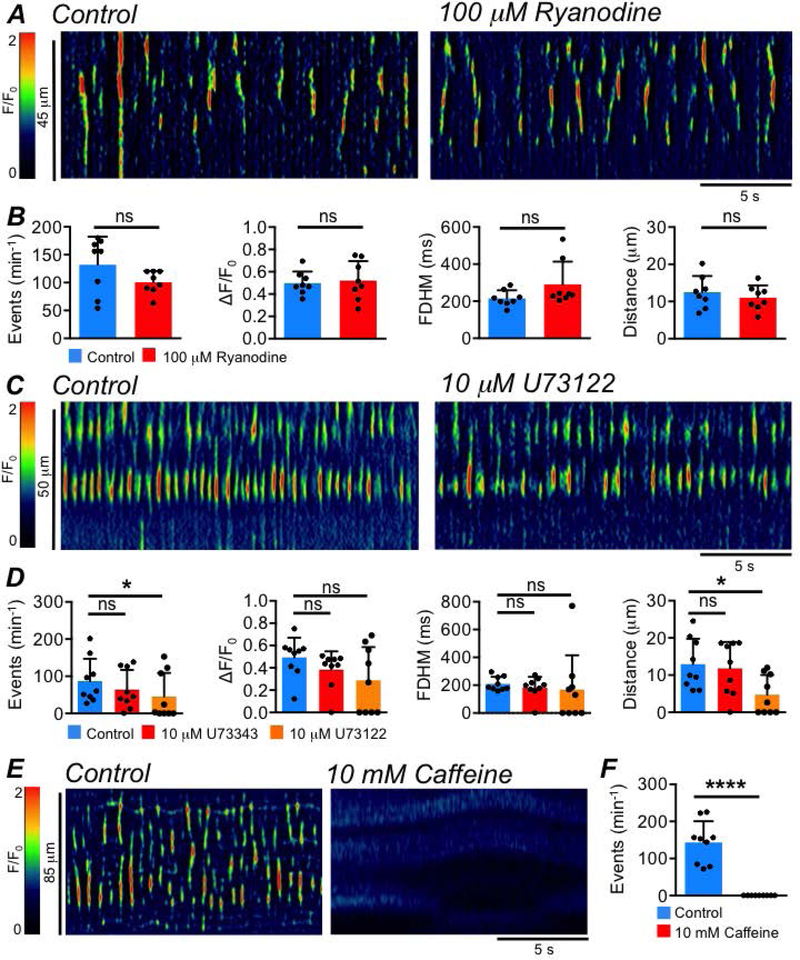
A STMs showing the effect of the ryanodine receptor antagonist, ryanodine (100 μM), on ICC-SS Ca2+ transients. B Summary data showing the effect of ryanodine on ICC Ca2+ transient frequency, amplitude, duration and spatial spread, c=8, n=3. C STMs showing the effect of the PLC inhibitor, U73122 (10 μM), on ICC-SS Ca2+ transients. D Summary data showing the effect of U73122 and its inactive analogue, U73343 (10 μM), on ICC Ca2+ transient frequency, amplitude, duration and spatial spread, c=9, n=3. E STMs showing the effect of caffeine (10 mM) on ICC-SS Ca2+ transients. F Summary effect of caffeine on ICC-SS Ca2+ transient frequency, c=9, n=5.
