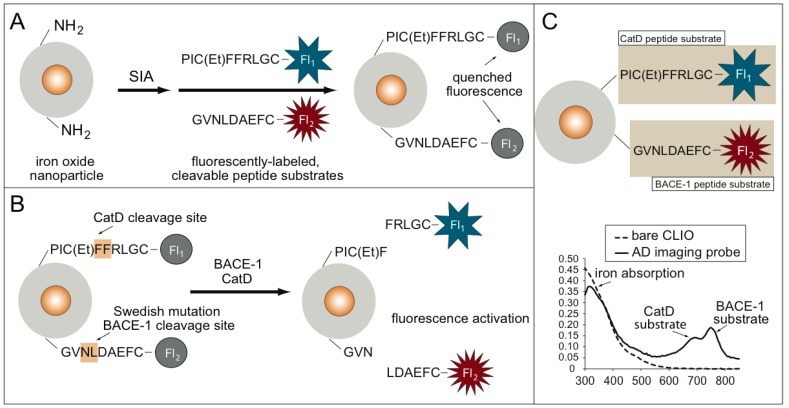
Figure 1.
(A) Synthesis of the Alzheimer’s disease (AD) imaging probe using an iron oxide nanoparticle scaffold and fluorescently-labeled peptide substrates for cathepsin D (CatD) and cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) AD enzymatic biomarkers. (B) Fluorescence activation of the AD imaging probe. Fluorescence is quenched until either the presence of CatD or BACE, which cleaves the fluorescence substrates, results in a fluorescence signal increase. (C) UV–VIS spectrum data confirm the synthesis of the AD molecular imaging (MI) probe.