Fig 2.
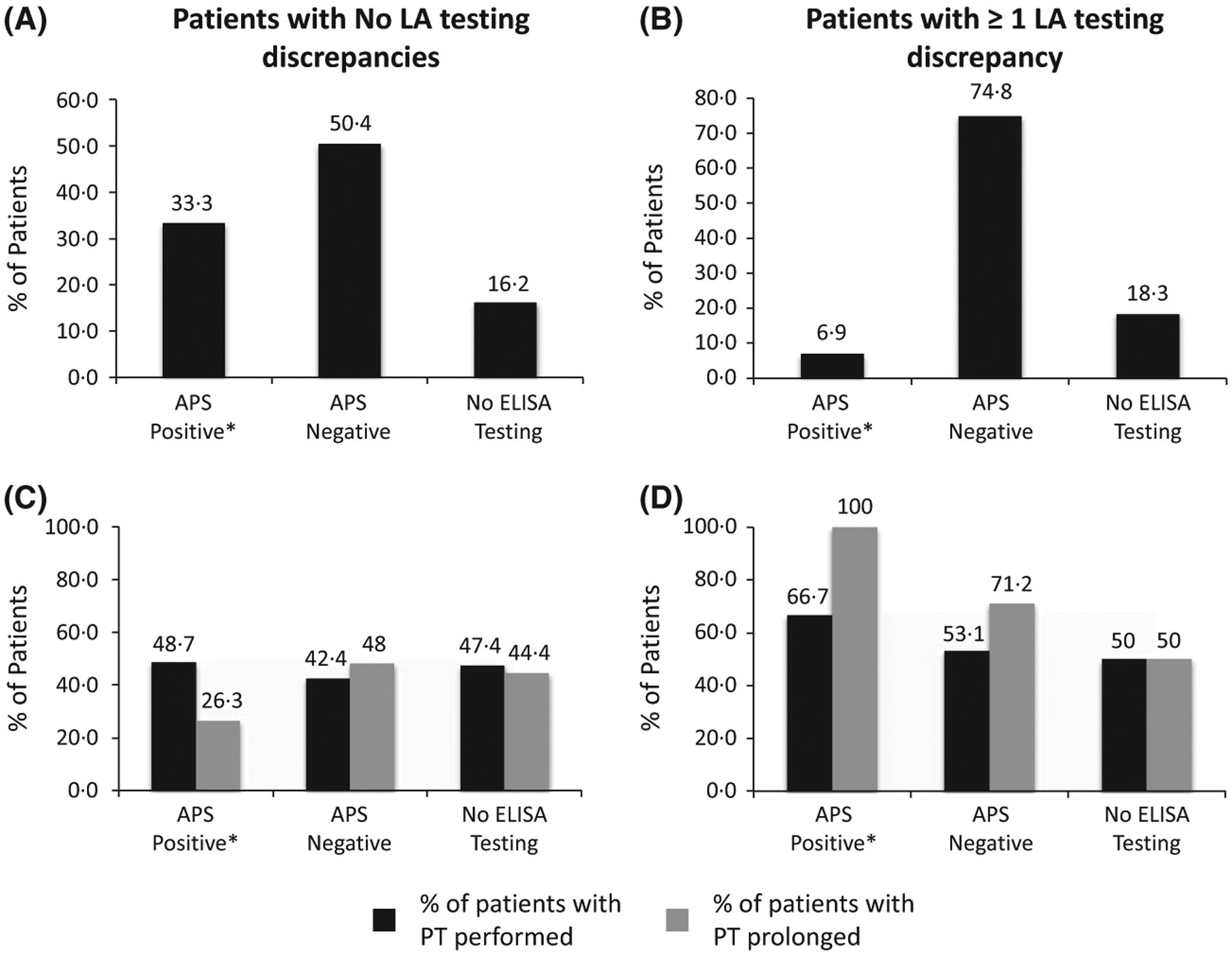
Comparison between consistently positive and discrepant LA results utilizing immunological APS test results in patients (n = 248) with PTT prolongation (not due to heparin or factor deficiency, as noted in the text). Plots A and C represent patients with consistently positive LA results: (A) 33·3% (39/117) APS-positive, 50·4% (59/117) APS-negative, and 16·2% (19/117) with no ELISA testing. (C) PT was performed in 48·7% (19/39) APS-positive, 42·4% (25/59) APS-negative and 47·4% (9/19) with no ELISA testing. Of those tested, 26·7% (5/19), 48% (12/25) and 44·4% (4/9) of the PTs were prolonged, respectively. Plots B and D represent patients with discrepant LA results: (B) 6·9% (9/131) APS-positive, 74·8% (98/131) APS-negative and 18·3% (24/131) with no ELISA testing. (D) PT was performed in 66·7% (6/9) APS-positive, 53·1% (52/98) APS-negative and 50% (12/24) with no ELISA testing. Of those tested, 100% (6/6), 71·2% (37/52) and 50% (6/12) of the PTs were prolonged, respectively. Note: Immunological APS studies [anticardiolipin (aCL) and β−2-glycoprotein-I (β2GPI), both IgG and IgM antibodies] were measured by ELISA (QUANTA LiteTM; Inova Diagnostics Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). Positivity for APS (manufacturer’s recommendations) was modified from the Sapporo criteria (Miyakis et al, 2006) and defined as an aCL antibody of IgG and/or IgM isotype with titres >40 IgG antiphospholipid units (GPL) or IgM antiphospholipid units (MPL). The β2GPI antibody titres of IgG and/or IgM isotypes were defined by titres >20 GPL or MPL. APS, antiphospholipid syndrome; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; LA, lupus anticoagulant; PTT, partial thromboplastin time; PT, prothrombin time.
