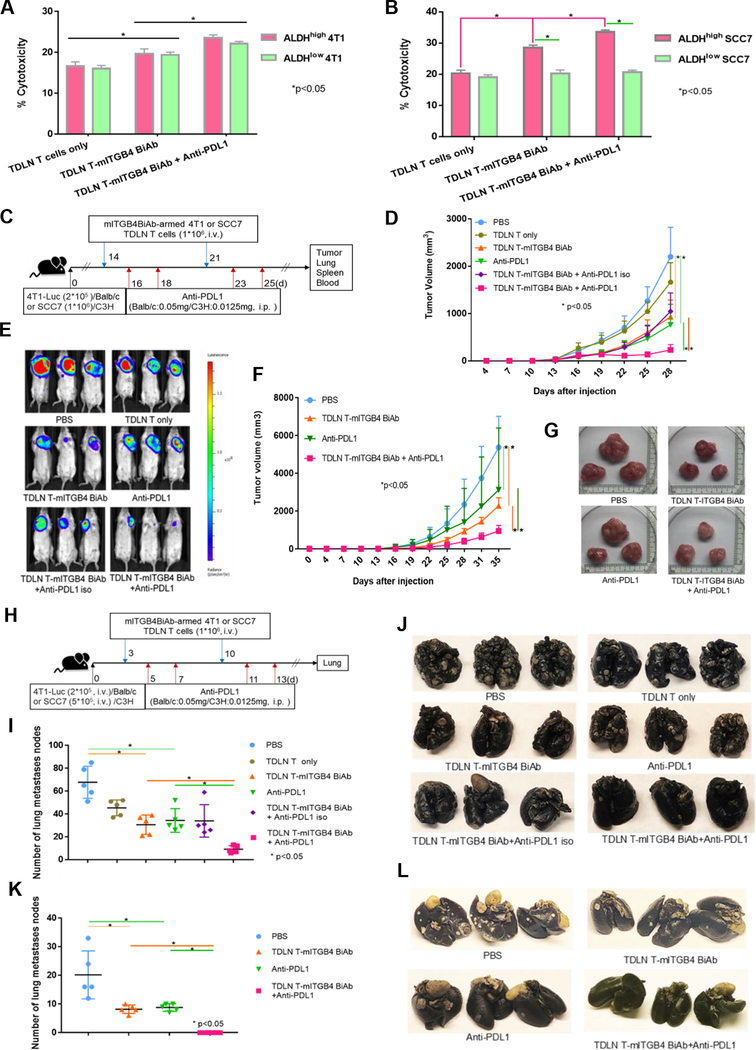
Figure 3.
ITGB4-targeted immunotherapy using mITGB4 BiAb-armed TDLN T cells via adoptive transfer. A, B: In vitro CTL activity of TDLN T cells co-cultured with 4T1 (A) and SCC7 (B) ALDHhigh vs. ALDHlow populations. C: Experimental protocol of the therapeutic 4T1 and SCC7 established (day 14) tumor models by adoptive transfer of mITGB4 BiAb-armed T cells. Treatment groups included: PBS, TDLN T cells, TDLN T-mITGB4 BiAb, anti-PD-L1, TDLN T-mITGB4 BiAb + anti-PD-L1 isotype, and TDLN T-mITGB4 BiAb + anti-PD-L1(n=5). D: TDLN T-mITGB4 BiAb significantly inhibited tumor growth in therapeutic 4T1 model, which was enhanced by anti-PD-L1. E: Luminescence imaged by IVIS at the end of experiments to display tumor size in treated mice of the therapeutic 4T1 model. F, G: In therapeutic SCC7 model, TDLN T-mITGB4 BiAb inhibited tumor growth, and co-injection and anti-PD-L1 significantly boosted the therapeutic effectiveness. H: Experimental lung metastasis protocol. I-L: In both 4T1 and SCC7 experimental lung metastasis models, TDLN T-mITGB4 BiAb significantly suppressed the metastases. Statistics (I) and representative photos (J) of 4T1 tumors from treated Balb/c mice are shown. Statistics (K) and representative photos (L) of SCC7 tumors from treated C3H mice are shown. The therapeutic experiments on 4T1 and SCC7 local tumors were repeated three times.