Figure 5. Model of C9ORF72 loss‐of‐function and DPR gain‐of‐function toxicity.
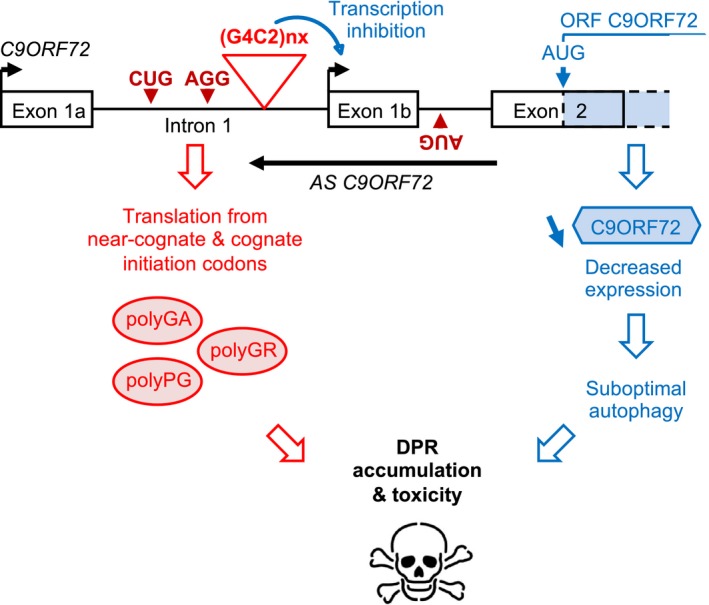
Expanded sense G4C2 and antisense C4G2 repeats are translated into polyGA, polyGR, and polyPG DPR proteins through initiation to near‐cognate codons or a cognate ATG codon embedded in a poor Kozak sequence. Concomitantly, expanded G4C2 repeats promote epigenetic DNA changes that inhibit promoter 1b activity, ultimately resulting in decreased expression of the C9ORF72 protein. Reduced expression of C9ORF72 leads to suboptimal autophagy that promotes the toxic accumulation of polyGA, polyGR, and polyPG DPR proteins, ultimately resulting in neuronal cell death.
