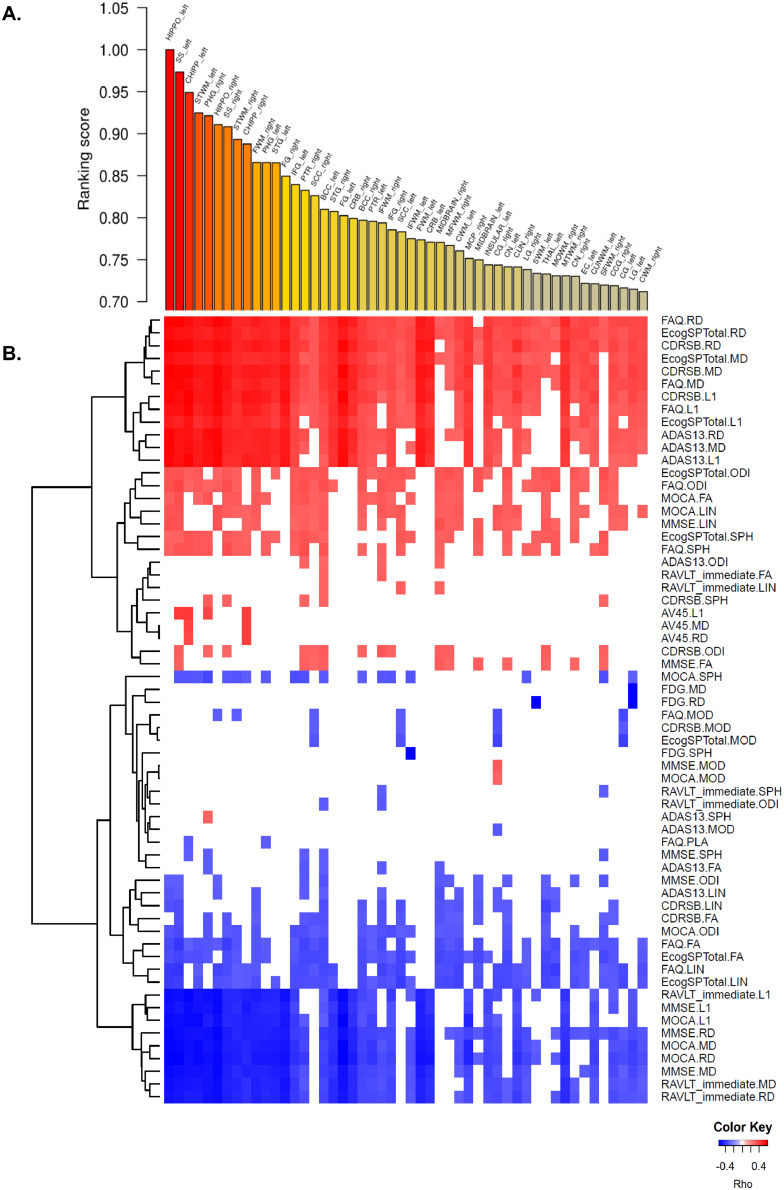
Fig. 2.
A) Rank-ordered brain regions according to the extent of association to the clinical/cognitive features. B) Heatmap of the correlations between clinical/cognitive traits and DTI-derived features. Cognitive and pathological traits with DTI-derived features are listed on the right axis, while the top 50 brain regions are listed across the top axis. The intensity of the color in each cell indicates the magnitude of the Spearman's rank correlation coefficient between the corresponding row and column variables, for those correlations with adjusted pvalues < 0.05. Red indicates positive correlation; blue indicates negative correlation. Fluorodeoxyglucose (18F) (FDG)-PET; Florbetapir (AV-45) PET, Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS-Cog), Mini–Mental State Examination (MMSE), Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (RAVLT), Functional Activities Questionnaire (FAQ), and Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) and Clinical Dementia Rating Sum of Boxes (CDRSB), clinical and cognitive performance scores, self (PT)- and informant (SP)- everyday cognition (ECog) memory scores, Fluorodeoxyglucose (18F) (FDG)-PET and Florbetapir (AV-45) PET. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)