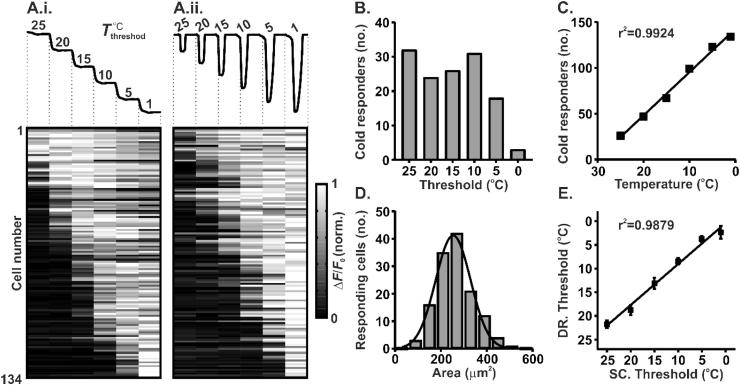
Fig. 3.
In vivo calcium imaging of dorsal root ganglia reveals variable thermal activation thresholds of cold-sensing neurons (Luiz et al., 2019). (A) Normalised fluorescence response from 134 cold-sensitive neurons expressing GCaMP3 following a staircased (A.i.) or drop temperature stimulus (A.ii.). The cooling protocols are shown at the top of the figure. Each row represents the response from the same neuron to each stimulus protocol. (B) Summary of the threshold of cold-sensing neuron activation observed following a staircased cooling protocol as in (A.i.). (C) Number of neurons activated by different cooling temperature drops as in (A.ii.) (linear regression: y = − 4.715 ∗ x + 142.4). (D) Histogram of cell area for cold-sensing neurons (Least squares Gaussian; Bin width is 60 μm2; Mean = 253.6 μm2, Std. Dev. 76.06 μm2). (E) Relationship between mean thresholds of activation in response to a drop (DR) cooling stimulus versus a staircased (SC) cooling stimulus (linear regression: y = 0.8652 ∗ x + 0.3839). Error bars denote S.E.M.