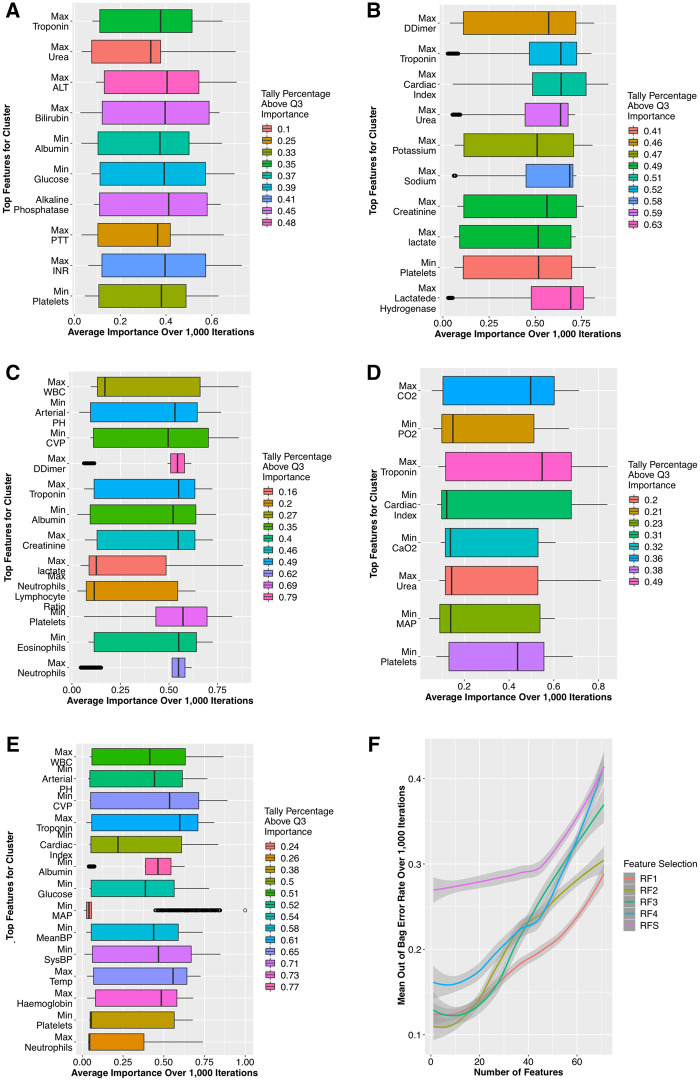
Figure 3.
Feature selection results: (A) FS1 comprises high-profile hepatic and coagulation indicators (including bilirubin, Alanine transaminase [ALT], and the International Normalised Ratio [INR]); (B) FS2 features mainly comprise cardiovascular (troponin, lactate, d-dimer) and renal (creatinine, potassium, and urea) indicators; (C) FS3 features are relevant to all SOFA subcomponents, reflecting the heterogeneity of the minimal organ dysfunction; (D) FS4 features are of respiratory (CO2, CaO2, and PO2), and cardiovascular relevance (including mean arterial pressure [MAP]). (E) In contrast, FSS includes a portion FS1–FS4, but largely consists of general signs of deterioration (eg, systolic blood pressure, temperature, white blood cell count [WBC]), which have been found to be good indicators of mortality but nondiscriminative between septic and nonseptic patients.31 (F) shows the out-bag-error rates over 1000 iterations of bootstrapped feature selection.