Fig. 6.
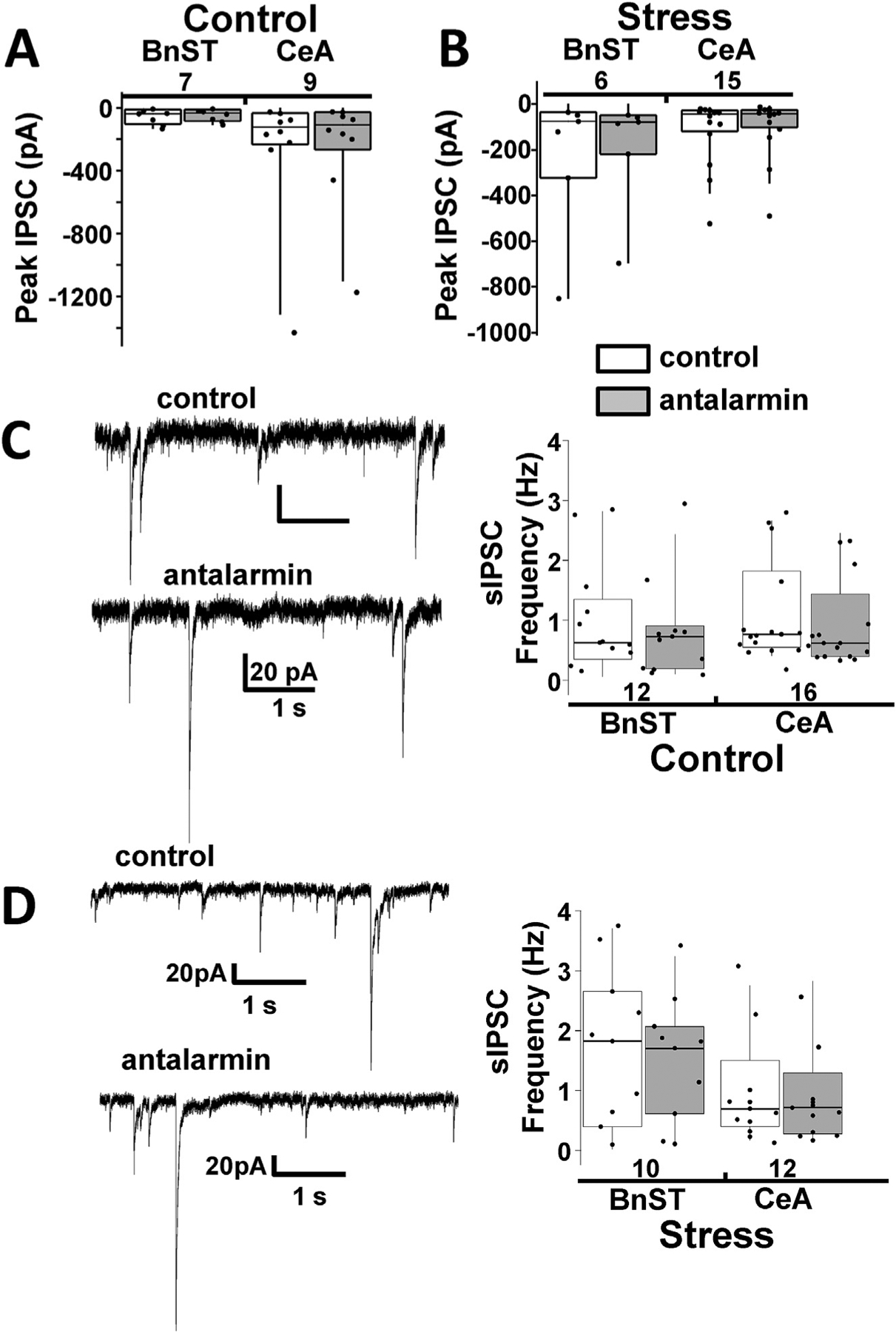
CRF R1 receptor antagonists do not significantly affect spontaneous IPSCs in control or stressed mice (A) Summary box and whisker plots comparing the peak IPSC in the absence (control, white) and presence (gray) of 25 μM antalarmin, a CRF receptor antagonist, for 400 ms light evoked IPSCs from CRF− neurons from the BnST (left) or CeA (right). (B) Same data plotted from CRF− lacking neurons exposed to stress protocols. The numbers below the brain region description indicate number of neurons tested. (C) Example voltage clamp recordings (left) from unidentified CRF− lacking neurons in the BnST illustrating spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSCs) in the absence (control) and presence of a CRF R1 antagonist (antalarmin). Summary box and whisker plots (right) comparing the lack of a pharmacological effect in BnST and CeA. (D) Same data plotted from CRF− lacking neurons exposed to stress protocols. The numbers above the brain region description indicate number of neurons tested.
