Figure 6.
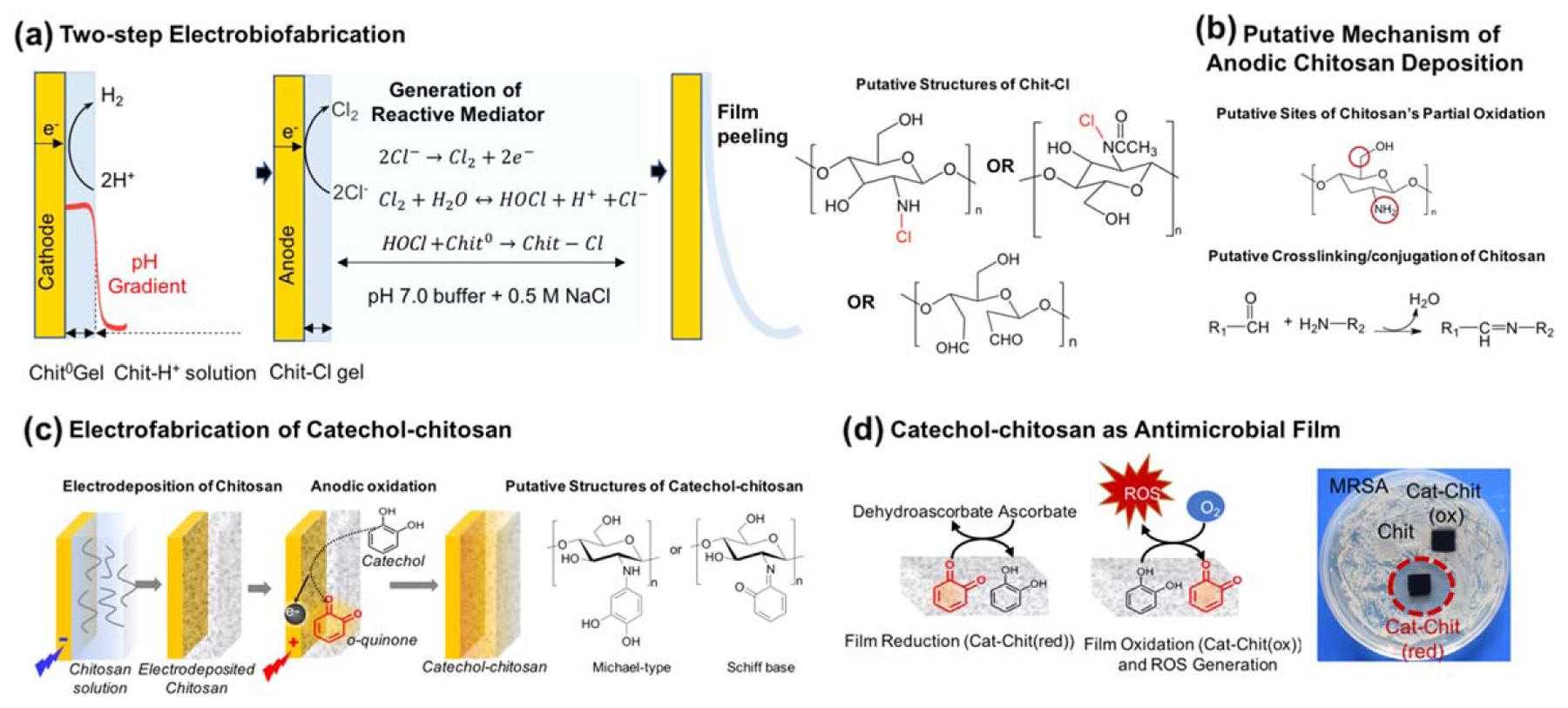
Anodic (oxidative) deposition of chitosan involves covalent modifications. (a) Two-step fabrication of chitosan film to obtain chloramine residues that confer antimicrobial activities. (b) An analogous single step anodic deposition mechanism for chitosan. (c) The anodic fabrication of a catechol–chitosan film. Adapted from [239]. CC BY 4.0. (d) Catechol–chitosan films are redox-active and allow for the sustained in situ generation of ROS that can inhibit the growth of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Adapted from [240]. Copyright 2018, with permission from Elsevier.
