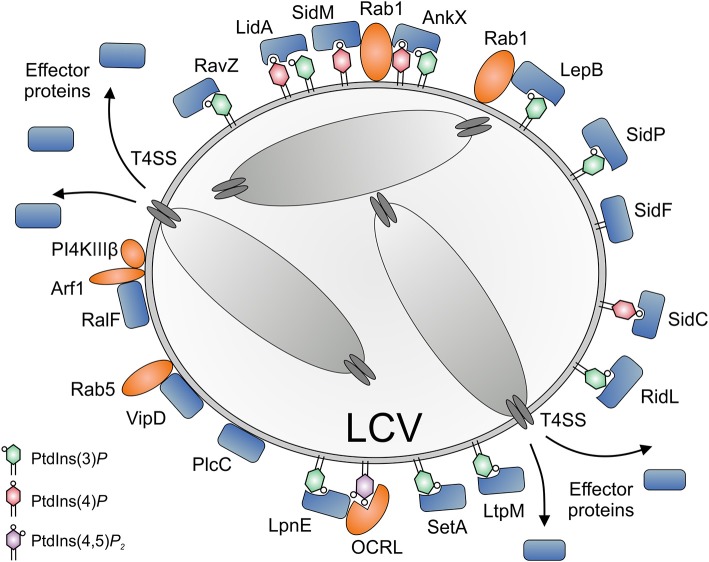
Figure 4.
Subversion of host PI lipids by L. pneumophila effector proteins. L. pneumophila effector proteins translocated by the Icm/Dot T4SS subvert PI lipids on the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV) (i) by directly binding PIs (SidC, SidM, AnkX, LidA, RidL, SetA, LtpM), (ii) by acting as bacterial PI phosphatases (SidF, SidP), PI kinases (LepB, LegA5), or phospholipases (VipD, PlcC, LpdA), or (iii) by recruiting eukaryotic PI phosphatases or kinases (RalF, SidM). PtdIns(4)P is bound by SidC (ubiquitin ligase) and SidM (Rab1 GEF/AMPylase). LidA and the Rab1 phosphocholinase AnkX bind PtdIns(3)P as well as PtdIns(4)P. PtdIns(3)P is bound by RidL (retromer inhibitor) and RavZ (Atg8/LC3 protease), as well as by SetA and LtpM (glycosyltransferases) and LepB (Rab1 GAP, PI 4-kinase). SidF and SidP are PI 3-phosphatases. VipD and PlcC function as a Rab5-activated phospholipase A1 or a Zn2+ metallophospholipase C, respectively. LpnE is secreted by an unknown mechanism and binds PtdIns(3)P as well as the host PI 5-phosphatase OCRL. The GEF RalF activates the small GTPase Arf1, which in turn recruits the host PI 4-kinase IIIβ (PI4KIIIβ). OCRL and PI4KIIIβ produce PtdIns(4)P from PtdIns(4,5)P2 or PtdIns, respectively.