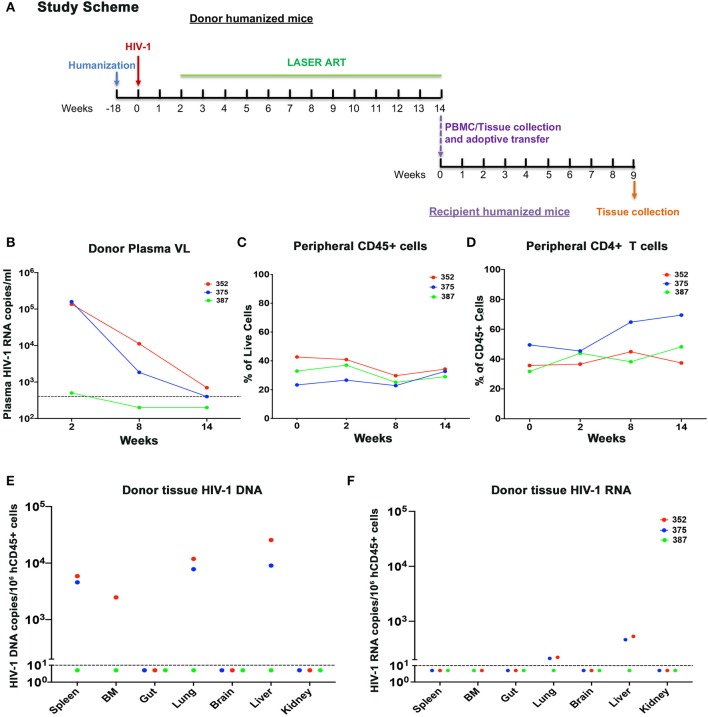
Figure 4.
Adoptive transfer of donor humanized mice with undetected or close-to-detection limit viral load. (A) The experimental scheme. In brief, donor humanized mice were first infected with HIV-1ADA for 2 weeks. Animals were then maintained under LASER ART which contained a combination of nanoformulated long-acting named NMCAB, NMABC, NM3TC, and NRPV for 3 months until pVL reached undetectable level or close to detection limit of 400 HIV-1 RNA copies/ml. Donor humanized mouse splenocytes and PBMCs were extracted and separately engrafted to respective naïve humanized mice. The recipient animals were maintained for 9 weeks to monitor HIV-1 recovery. The dynamic changes of individual donor humanized mouse were recorded for (B) pVL, (C) peripheral human CD45+, and (D) peripheral human CD4+ T cells. (E) Tissue HIV-1 DNA and (F) tissue HIV-1 RNA in individual donor humanized mice was evaluated across spleen, BM, gut, lung, brain, liver, and kidney, using semi-nested real time qPCR. The dotted line in (B) indicated the detection limit (DL) of 400 HIV-1 RNA copies/ml. The dotted line in (E,F) showed the DL below 10 HIV-1 copies/106 human CD45+ cells.