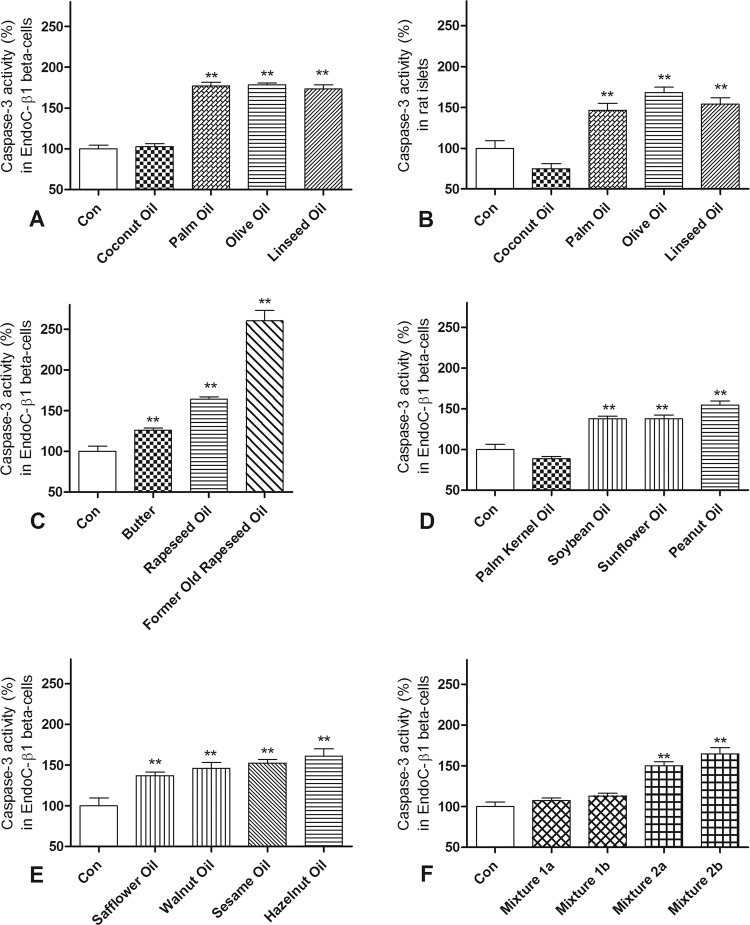
Fig. 1. Toxicity of different FFA compositions mimicking popular edible plant oils and butter as well as selected mixtures of them in human EndoC-βH1 beta-cells and rat islets.
Human EndoC-βH1 beta-cells (a) and isolated rat islets (b) were incubated for 2 days with compositions of different FFAs (total concentration 500 µM each) simulating the most popular edible plant oils. In addition EndoC-βH1 beta-cells were incubated with further FFA compositions mimicking additional edible oils and butter (c–e) as well as with mixtures composed of equal volumes of selected FFA compositions (f). Mixture 1a contained the FFA compositions mimicking coconut oil, olive oil, linseed oil, and palm oil while mixture 1b was composed of the FFA compositions mimicking palm kernel oil, soybean oil, sunflower oil, and safflower oil. Mixture 2a contained the FFA compositions mimicking rapeseed oil, sesame oil, peanut oil, and walnut oil whereas mixture 2b was made of the FFA compositions mimicking linseed oil, soybean oil, rapeseed oil, and walnut oil. After incubation activation of caspase-3 was measured. Data are expressed as means ± SEM of 4–9 independent experiments. **p < 0.01 compared to untreated cells (Dunnett’s Multiple Comparison Test).