Figure 1.
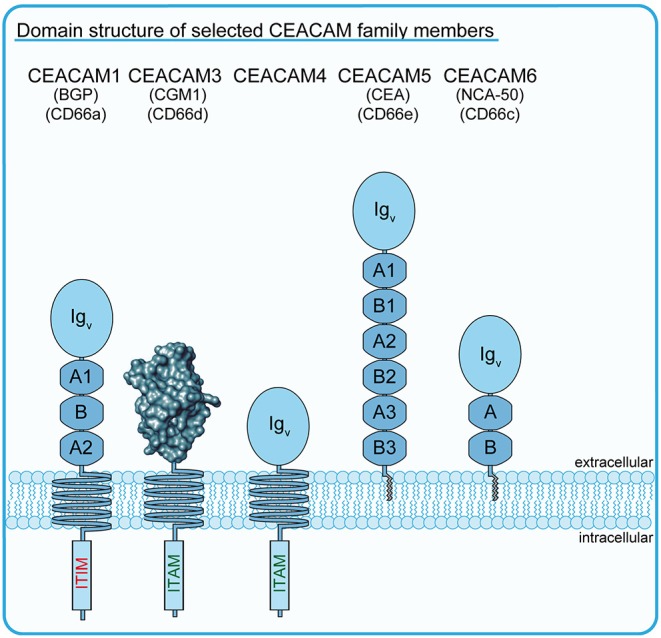
Schematic drawing of selected members of the human CEACAM family. Schematic outline of several members of the human carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-related cell adhesion molecule (CEACAM) receptor family. All CEA-related proteins belong to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily and are characterized by the possession of a homologous amino-terminal Ig variable (IgV)-like domain, which is depicted in the case of CEACAM3 as a rendered protein surface according to Bonsor et al. (7). The blue circles indicate the IgV-like domains of CEACAMs other than CEACAM3, while the blue octagons indicate additional Ig constant 2 (IgC2)-like domains occurring in different numbers in particular family members. The transmembrane helices of CEACAM1, CEACAM3, and CEACAM4 connect the extracellular Ig-domains with functional ITIM (CEACAM1), ITAM-like (CEACAM3), or consensus ITAM sequences (CEACAM4). GPI-anchors of CEACAM5/CEA and CEACAM6 are depicted in gray.
