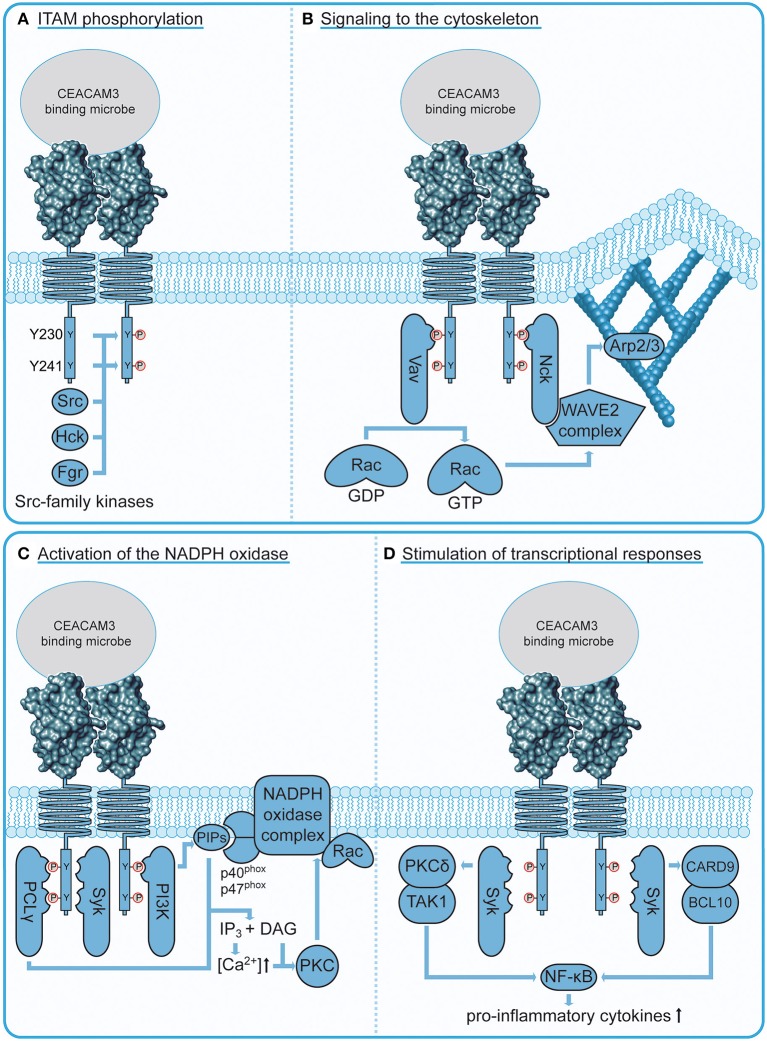
Figure 3.
CEACAM3 signaling connections. (A) Phosphorylation of CEACAM3 upon bacterial engagement. Localized clustering of CEACAM3 receptors by multivalent, CEACAM-binding bacteria trigger recruitment and activation of several Src family tyrosine kinases, which in turn phosphorylate the ITAM-like sequence in the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor at two tyrosine residues (Y230 and Y241). This phosphorylation event is critical for downstream signaling processes. (B) CEACAM3 signaling to the cytoskeleton. The adaptor protein Nck binds via its SH2 domain to the membrane proximal CEACAM3 phosphotyrosine residue pY230 and recruits the WAVE2 complex to sites of bacterial attachment. Activation of this complex requires a localized increase in GTP-loaded Rac, which is orchestrated by recruitment of the Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor Vav. Similar to Nck, Vav binds via its SH2 domain to CEACAM3 pY230. Activation of the WAVE2 complex leads to localized activation of Arp2/3 at the site of infection resulting in particle engulfment by actin cytoskeleton-based lamellipodial protrusions. (C) CEACAM3 signaling to the NADPH oxidase. Residue pY230 serves as an interaction platform for the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3′ kinase (PI3K). PI3Ks are responsible for the generation of phosphoinositides (PIPs), which regulate the oxidative burst by recruitment of NADPH oxidase subunits p40phox and p47phox. In addition, PIP hydrolysis by CEACAM3-recruited phospholipase C γ (PLCγ) releases the second messengers inositol-(1,4,5)-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacyl glycerol (DAG). Together, they activate the protein kinase C (PKC), which further stimulates the NADPH oxidase complex. (D) CEACAM3 stimulation of neutrophil transcriptional response. CEACAM3 can trigger the NF-κB-mediated transcriptional regulation of IL-8 and other neutrophil chemotactic factors. CEACAM3-initiated NF-κB activation occurs via two distinct routes: the PKCδ/TAK1 pathway and the CARD9/BCL10 pathway depend on Syk localization to phosphorylated CEACAM3.