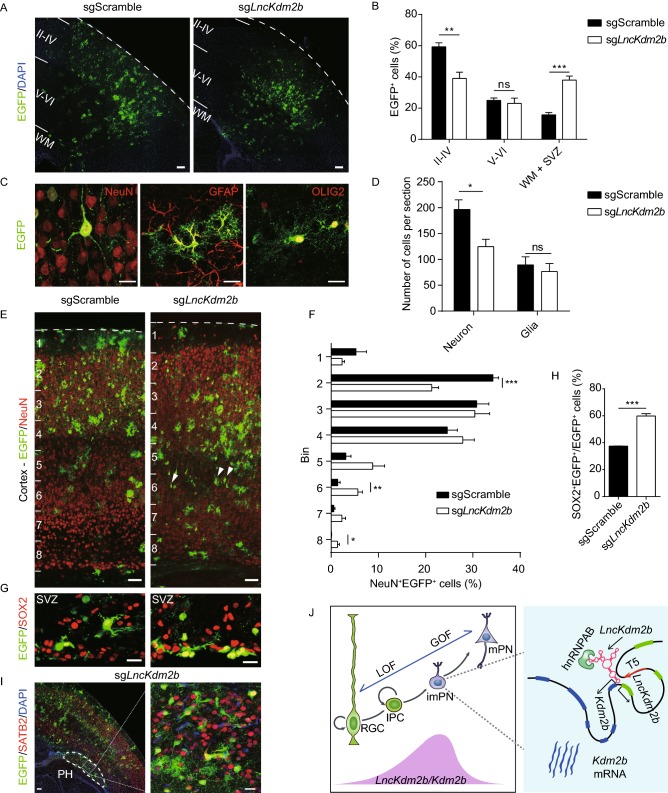
Figure 7.
LncKdm2bregulates cortical neuronal differentiation and migration. E13.5 mouse cortices were electroporated with piggyBac-CRISPR/Cas9 vectors and brain sections were analyzed at P10. (A–C) Representative images showing distribution of EGFP+ cells in cortices at P10 (A). The relative locations of EGFP+ cells were quantified (B). Four brains each. Examples of EGFP+ cells with neuronal and glial morphology were positive for SATB2, GFAP and OLIG2 respectively (C). (D) Quantification of EGFP+NeuN+ neurons and EGFP+ glial cells at P10. Four brains each. (E and F) Neuronal migration was analyzed at P10 by quantifying percentiles of NeuN+EGFP+ neurons in each bin. Arrowheads indicate delayed projection neurons. Four brains each. (G and H) Representative images of SOX2 immunofluorescent staining in the SVZ (G). SOX2+EGFP+ cells were quantified (H). Three brains each. (I) The periventricular heterotopias (PH) are evident in sgLncKdm2b-electroporated cortices. Enlarged boxed area at the right shows SATB2+ projection neurons in the PH. (J) A model for LncKdm2b promoting cortical neurogenesis by cis-activating Kdm2b. LncKdm2b and Kdm2b are transiently expressed in freshly born projection neurons. LncKdm2b RNA facilitates an open chromatin configuration locally by bringing together the upstream regulatory cis-element T5, Kdm2b promoter and hnRNPAB to maintain Kdm2b’s transcription. In (B), (D), (F), and (H), quantification data are shown as mean + SEM. In (B), (D), (F), and (H), statistical significance was determined using 2-tailed Student’s t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, “ns” indicates no significance. In (A), (E), and (I, left), scale bars, 100 μm. In (C), (G), and (I, right), scale bars, 20 μm. WM, white matter; SVZ, subventricular zone; PH, periventricular heterotopias; RGC, radial glial cells; IPC, intermediate progenitor cells; imPN, immature projection neurons; mPN, mature projection neurons; LOF, loss-of-function; GOF, gain-of-function