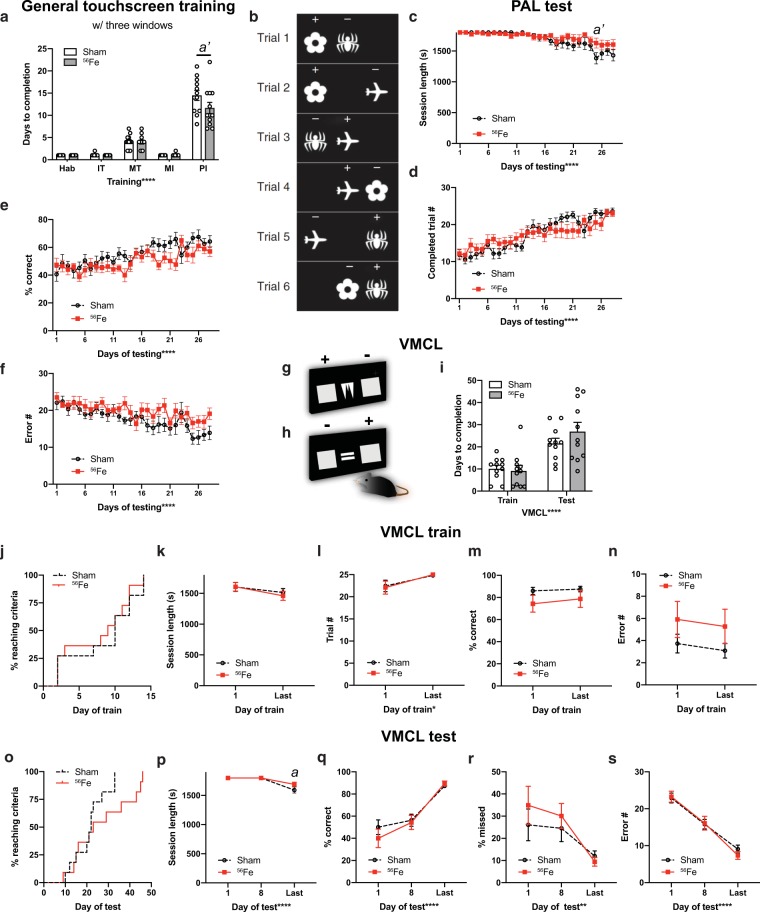
Figure 3.
Mice exposed to 56Fe IRR at 6-month of age complete the final stage of general touchscreen testing in fewer days than Sham mice, but perform similarly to Sham in tests of rule-based learning and stimulus-response habit learning. (a) Sham and 56Fe IRR mice performed similarly in the 4 first steps of general touchscreen training stages with three windows, including Habituation (Hab), Initiate Touch (IT), Must Touch (MT), and Must Initiate (MI). However, 56Fe IRR mice completed the Punish Incorrect (PI) stage of general touchscreen training in fewer days than Sham mice. (b) Sample touchscreen images for Paired Associates Learning (PAL). (c–f) Sham and 56Fe IRR mice performed similarly in PAL. (c) session length, (d) completed trials, (e) percent (%) correct, (f) Error number (#). (g,h) Sample touchscreen images for Visuomotor Conditional Learning (VMCL) train and test phases. (i) Sham and 56Fe IRR mice performed similarly in VMCL train and test. (j) Cumulative distribution function showed no difference in days required to complete training. Distribution of Sham and 56Fe IRR mice (n = 11/group) did not differ in days required to complete VMCL training. (k–n) Sham and 56Fe IRR mice performed similarly in VMCL train. (k) session length, (l) completed trials, (m) % correct, (n) Error #. (o) Cumulative distribution function showed no difference in days required to complete VMCL test. Distribution of Sham and 56Fe IRR mice (n = 11/group) did not differ in VMCLtest. (p–s) Sham and 56Fe IRR mice performed similarly in VMCL test. (p) Session length, (q) % correct, (r) % missed, (s) Error #. Sham: n = 12 (a–f), 11 (i–s), IRR: 12 (a–f), 11 (i–s). Mean ± SEM. Two-way RM ANOVA in a,c–f,i,k–n,p–s, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, post hoc: Bonferroni a p < 0.05, a’ p < 0.01 in Sham vs. 56Fe; Mantel-Cox test in j,o.