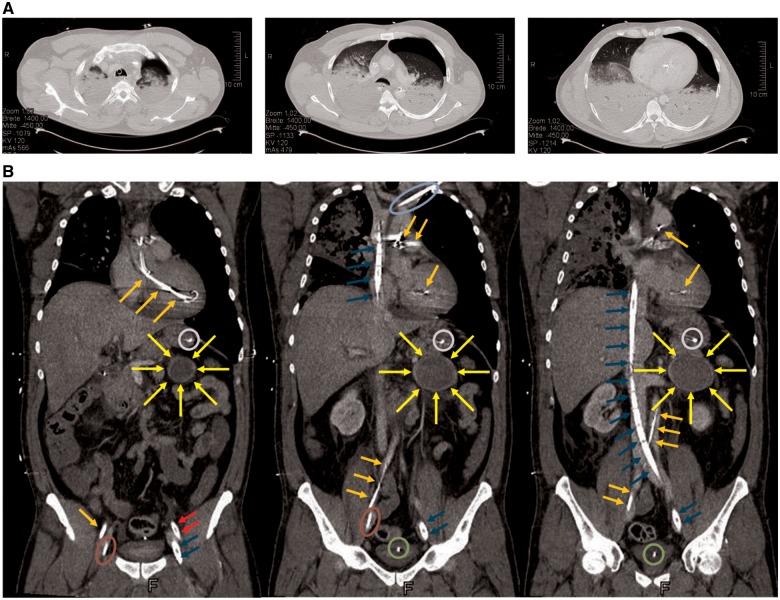
Figure 2.
Computed tomography of the thorax (A). Total dorsal consolidation of the lungs due to pulmonary oedema or secondary acute respiratory distress syndrome and a pneumothorax on the left side, which was caused by resuscitation. The pneumothorax was successfully evacuated by tube thoracostomy. Computed tomography of the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis (B). Imaging of a pheochromocytoma-suspected space-consuming lesion ( ) of the adrenal gland (diameter 6.7 cm) and the cannulization. Impella CP® optical (
) of the adrenal gland (diameter 6.7 cm) and the cannulization. Impella CP® optical ( ), veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation arterial cannula (
), veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation arterial cannula ( ), veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation venous cannula (
), veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation venous cannula ( ), Shaldon’s catheter (
), Shaldon’s catheter ( ), central venous catheter (
), central venous catheter ( ), urinary catheter (
), urinary catheter ( ), and feeding tube (
), and feeding tube ( ).
).