Figure 1.
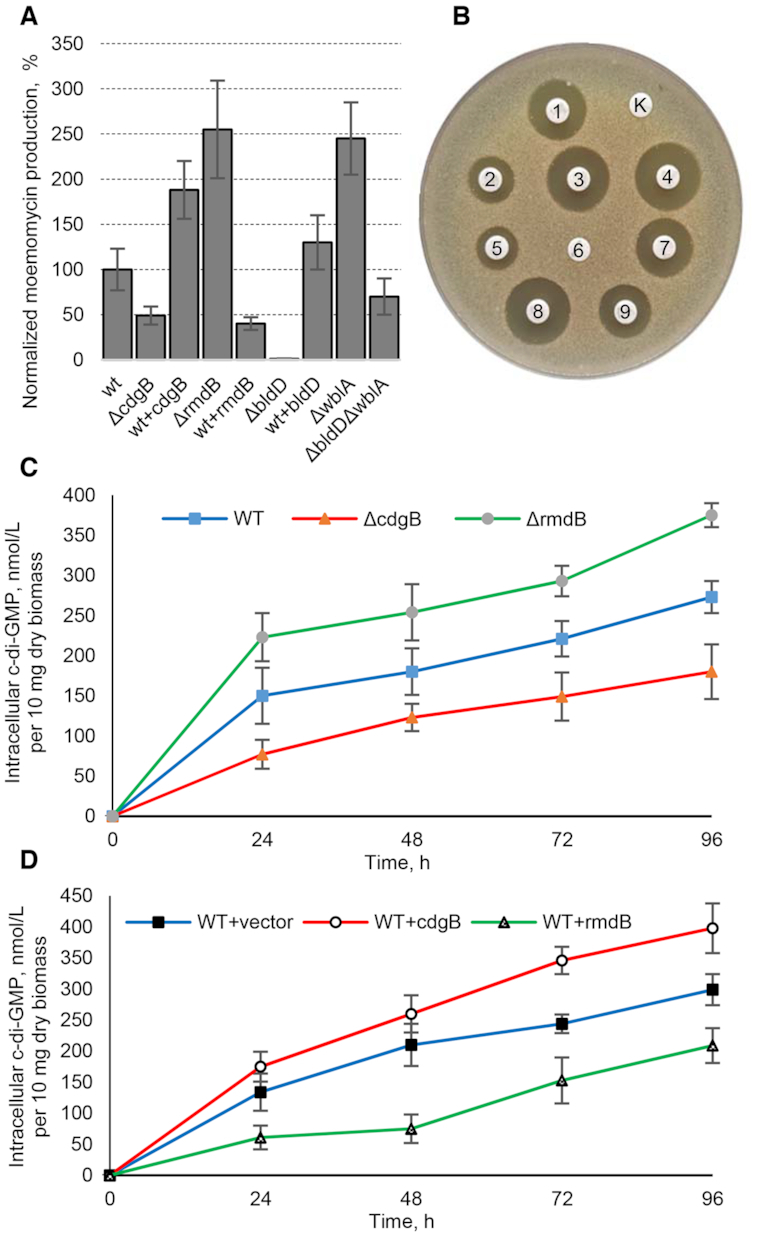
Levels of moenomycin and c-di-GMP production by various Streptomyces ghanaensis strains. (A) Moenomycin production titers by different S. ghanaensis strains studied in this work as determined by HPLC-MS. The mean value of moenomycin mass peak area in S. ghanaensis ATCC14672 was taken as 100%. Amounts of moenomycin were normalized to equal amounts of biomass (dry weight) and were mean values from at least three independent biological replicates. Error bars, ±2 SD. (B) Bacillus cereus growth inhibition around paper discs saturated with methanol extracts from equal amount of biomass of different MmA producers: S. ghanaensis ATCC14672 (1), ΔcdgBgh (2), ATCC14672 overexpressing cdgBgh (3), ΔrmdBgh (4), ATCC14672 overexpressing rmdBgh (5), ΔbldDgh (6), ATCC14672 overexpressing bldDgh (7), ΔwblAgh (8), ΔbldDghΔwblAgh (9), negative control, methanol (K). Intracellular c-di-GMP levels in the S. ghanaensis strains with gene deletions (C) and overexpressions (D). c-di-GMP was extracted at different time points from cells grown in TSB medium. Data represent means of three independent cultures and were normalized to equal amounts of dry biomass. Error bars are the standard deviations between independent cultures.
