Figure 1.
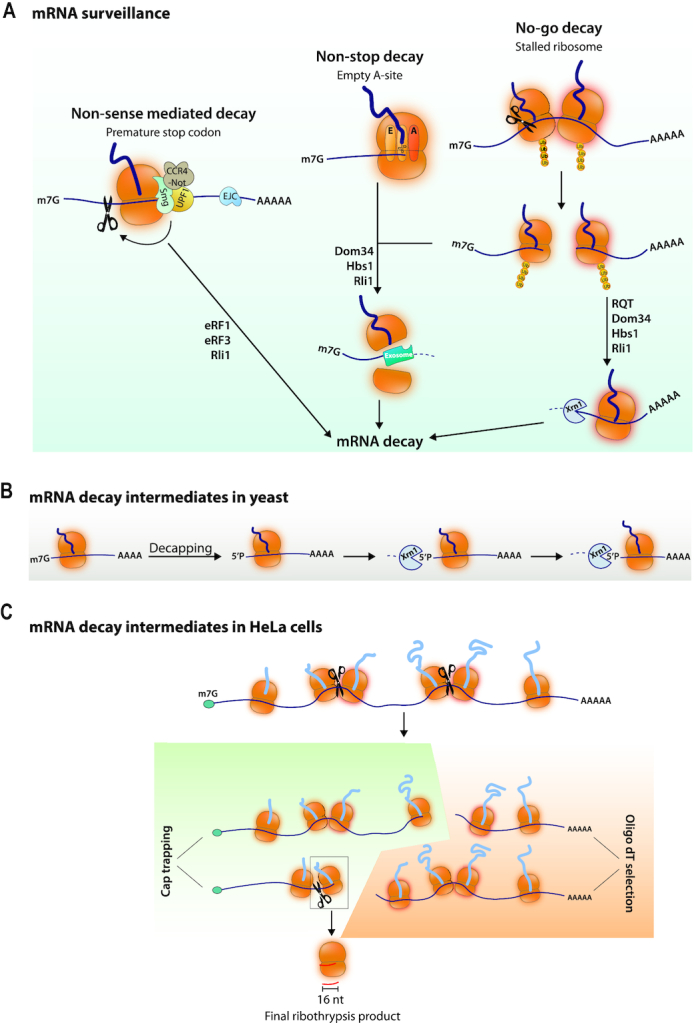
(A) mRNA surveillance induced mRNA decay. NMD occurs when mRNAs have a premature stop codon. In mammalian cells NMD works with Upf1, through the recruitment of the Smg5–7 proteins. Smg5 and Smg6 have a PIN domain associated with endonucleolytic activity and Smg6 has single stranded nuclease activity. Smg7 can recruit the Ccr4-Not deadenylase complex. Recognition of NMD substrates has to do with the distance from the real termination site where termination factors and the poly(A) binding protein are located and/or the presence of a downstream exon-junction complex (EJC). Substrates for NSD and NGD are either mRNAs on which the ribosomes will reach the end of the mRNA with an empty A site or where ribosomes stall. This will trigger ribosome collision that induces ribosomal subunit ubiquitination, endonucleolytic cleavage and exonucleolytic decay of the 5′ and 3′ mRNA fragments generated. The endonuclease has not been identified. The Dom34 and Hbs1 factors in yeast (called Pelota and Hbs1L and Gtpbp2 in mammals) recruited to empty A sites split ribosomes with the help of the Rli1 ATPase (called ABCE1 in human). Then the 5′ mRNA can be degraded by the exosome whereas the 3′ mRNA can be degraded by the Xrn1 5′ to 3′ exonuclease. In yeast an RQT complex contributes to ribosome splitting. (B) mRNA decay intermediates in yeast measure ribosome dynamics. Decapping produces 5′P mRNA ends that are substrates for the Xrn1 5′ to 3′ exonuclease. mRNA decay fragments of different lengths have 5′ ends showing 3-nucleotide periodicity. (C) mRNA decay intermediates in Hela cells. Purification of capped mRNAs and sequencing of their 3′ ends, or purification of poly(A) mRNAs and sequencing of their 5′ ends has revealed 3′ and 5′ ends respectively, within ORFs. The model is that ribosomes pause during translation elongation and this can create a ribosome collision, and then a chain of events similar to NGD called Ribothrypsis. The final product is a 16-nucleotide fragment resulting from the reiterated cleavage events.
