Figure 4.
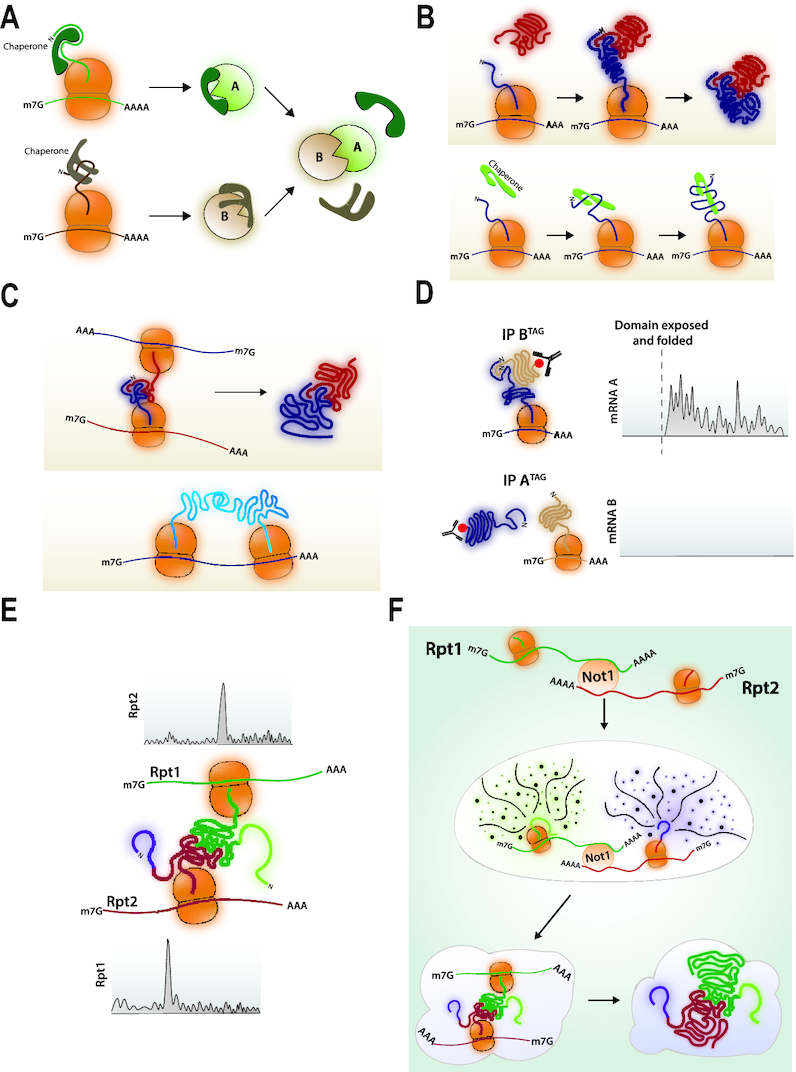
(A) Post-translational protein association. Proteins A and B are synthesized separately and kept soluble and assembly competent with dedicated chaperones that are released upon association of A and B. (B) Asymetric co-translational protein interaction. Upper panel: Protein B is produced, folded, released and recruited to the site of protein A translation. It associates with its domain of interaction in the nascent chain of protein A as soon as this domain folds. Lower panel: A chaperone is recruited to the site of translation of its client protein. (C) Co-translational assembly promoted by mRNA co-localization. Upper panel: The mRNAs encoding proteins A and B are tethered during translation so that the nascent chains of A can B can associate as soon as the interaction domains have folded and are exposed out of the tunnel. Lower panel: In the case of homo-oligomers, interaction of the nascent chains can occur from neighboring ribosomes on the same mRNA. (D) Asymetric co-translational protein interaction detected by ribosome profiling. Protein pairs known to interact are C-terminally tagged and immunoprecipitated. The ribosome footprints in the immunoprecipitate are recovered and aligned to the genome. They are detected with a sharp onset on the ORF of the mRNA encoding the partner subunit. This is asymmetric. (E) Co-translational association revealed by ribosome profiling. Ribosome pauses are detected by ribosome footprint accumulation on the RPT1 and RPT2 mRNAs that expose nascent chain-interacting domains outside of the ribosome tunnel. (F) Model for co-translational interaction of Rpt1 and Rpt2. mRNAs are first co-localized with the Not1 protein and dependent upon Not1. Then nascent chains emerging from the ribosome tunnel contribute to the formation of higher order granules in which paused ribosomes will be stable and assembly of nascent chain interacting domains can occur. After interaction, translation elongation resumes in the heavy particles.
