Figure 1.
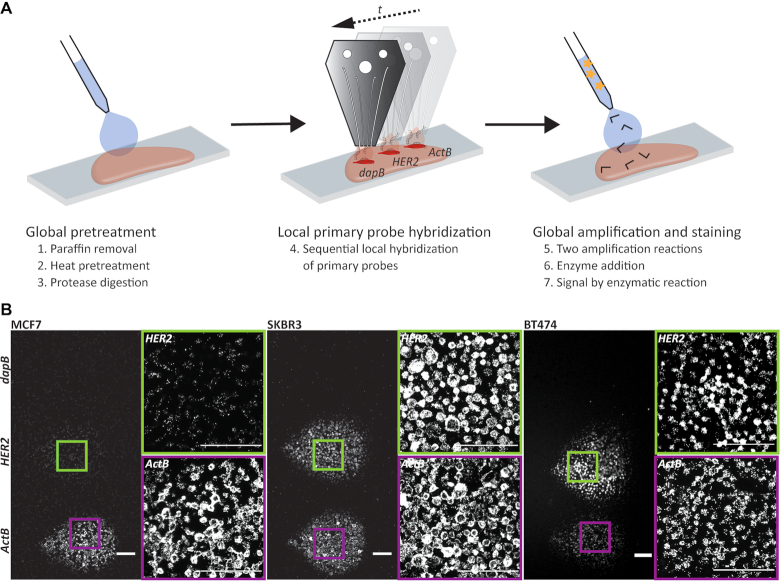
Local RNA in situ hybridization. (A) Schematic overview of a microfluidic implementation of chromogenic RNA in situ hybridization. The initial preparation of the tissue section including paraffin removal (1), heat (2) and protease (3) pretreatment, as well as fixation was performed globally. The primary probe was then hybridized locally to the RNA of interest (4). In this case the detection of HER2 is shown with internal negative (dapB) and positive (ActB) controls. Finally, the amplification of the signal using preamplifier and amplifier strands (5), the binding of enzyme (6), and the enzymatic reactions (7) were performed globally on the whole slide. (B) Fluorescence images of RNA-ISH experiments detecting the gene expression of HER2 in cell pellet sections of the breast cancer cell lines MCF7 (left), SKBR3 (center) and BT474 (right). Probes directed against bacterial dapB and ActB were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. Scale bar: 100 μm.