Figure 1.
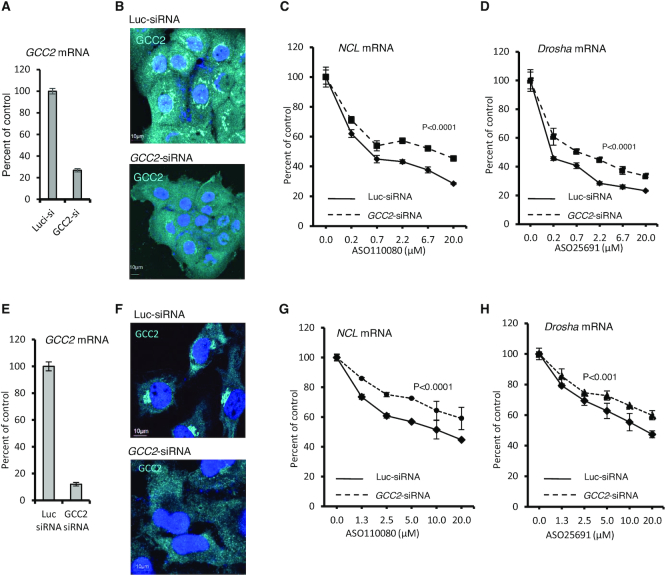
Reduction of GCC2 decreased ASO activity upon free uptake in different human cells (A) qRT-PCR quantification of GCC2 mRNA levels in A431 cells transfected with control luc-siRNA (targeting luciferase) or GCC2-specific siRNA for 72 h. (B) Immunofluorescent staining of GCC2 protein in A431 cells treated with siRNAs for 72 h. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 10 μm. (C and D) Levels of C) NCL and D) Drosha mRNAs determined by qRT-PCR in cells treated with siRNAs that were subsequently incubated for 24 h with PS-ASOs 110080 or 25691 targeting NCL or Drosha mRNAs, respectively. (E) qRT-PCR quantification of GCC2 mRNA levels in HeLa cells transfected with control siRNA or GCC2-specific siRNA for 72 h. (F) Immunofluorescent staining of GCC2 protein in HeLa cells treated with siRNAs for 72 h. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 10 μm. (G and H) qRT-PCR quantification for the levels of (G) NCL and (H) Drosha mRNAs in HeLa cells pretreated with siRNAs and were subsequently incubated for 24 h with PS-ASOs 110080 or 25691 targeting NCL or Drosha mRNAs, respectively. Error bars are standard deviations from three independent experiments. P-values were calculated based on F-test using Prism.