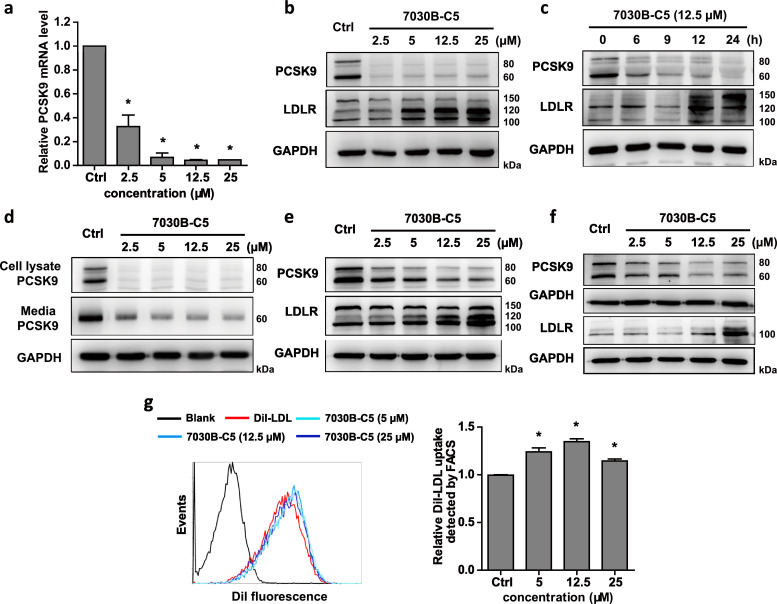
Fig. 2.
Effects of 7030B-C5 on PCSK9 and LDLR expression in hepatic cells. (a) HepG2 cells were treated with 7030B-C5 in a series of concentration for 24 h. The mRNA level of PCSK9 was measured by RT-qPCR analysis. (b) HepG2 cells were treated with 7030B-C5 in a series of concentration for 24 h. Expression of PCSK9 and LDLR protein was measured by Western blot. (c) HepG2 cells were treated with 7030B-C5 in 12.5 μM with different times. After treatment, cellular proteins were extracted and used to determine PCSK9 protein by Western blot. (d) HepG2 cells were treated with 7030B-C5 in a series of concentrations for 24 h. Secreted form of PCSK9 protein and cellular PCSK9 proteins were determined. (e) Huh7 cells were treated with different concentrations of 7030B-C5 for 24 h. Expression of PCSK9 and LDLR protein was measured by western blot. (f) Human primary hepatocytes were treated with 7030B-C5 for 24 h. Expression of PCSK9 and LDLR protein was determined. (g) HepG2 cells were treated with vehicle or 7030B-C5 for 24 h. The cells were incubated with DiI-LDL (5 μg/mL) at 37 °C for 4 h, and then the LDL uptake activity was measured by flow cytometric analysis. Values are presented as means ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.05 vs. control in the corresponding group.