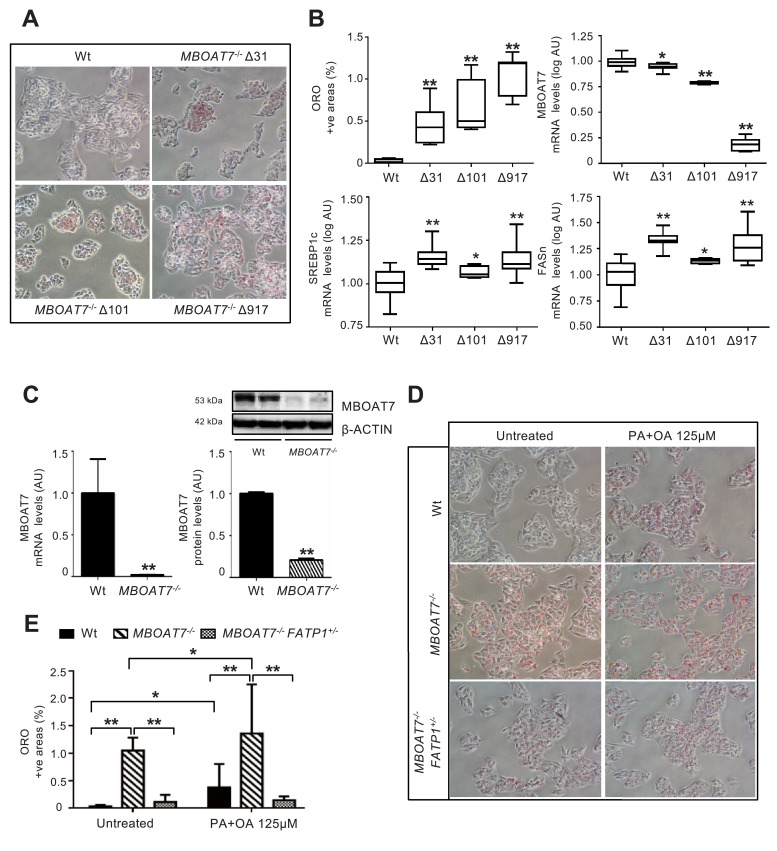
Fig. 5.
MBOAT7 deletion increases spontaneous fat accumulation in HepG2 hepatoma cells.
Spontaneous fat accumulation in untreated MBOAT7−/− cells carrying Δ31, Δ101 and Δ917 was evaluated by ORO staining (200X magnification) and quantified by ImageJ software in 10 random non-overlapping micrographs for each experimental condition, by calculating the percentage of pixels above the threshold value with respect to the total pixels per area. At least three independent experiments were conducted (A). Impact of MBOAT7 deletions on hepatic fat, and MBOAT7, SREBP1c, FASn mRNA, evaluated by qRT-PCR then normalized for β-actin (Arbitrary Units - AU). Boxes span from 25° to 75° percentile, while whiskers indicate the 10° and 90° percentile (B). * adjusted p<0.05, ** adjusted p<0.01 compared to wild-type (Wt) cells.
The Δ917 MBOAT7 deletion abrogates MBOAT7 expression, resulting in increased spontaneous fat accumulation, which was maintained after supplementation with palmitic and oleic acid (PA+OA 125 μM; ratio 1:2). mRNA levels were evaluated by qRT-PCR and protein levels by Western blot and then normalized for β-actin. For each condition, freshly protein lysates were pooled. All reactions were performed in duplicate in the same gel. **p<0.01 by two-tailed Student's t-tests (C). Lipid accumulation was evaluated by ORO staining (200X magnification) and quantified by ImageJ software in 10 random non-overlapping micrographs for each experimental condition, by calculating the percentage of pixels above the threshold value with respect to the total pixels per area. At least three independent experiments were conducted. * adjusted p<0.05, ** adjusted p<0.01 (D-E).