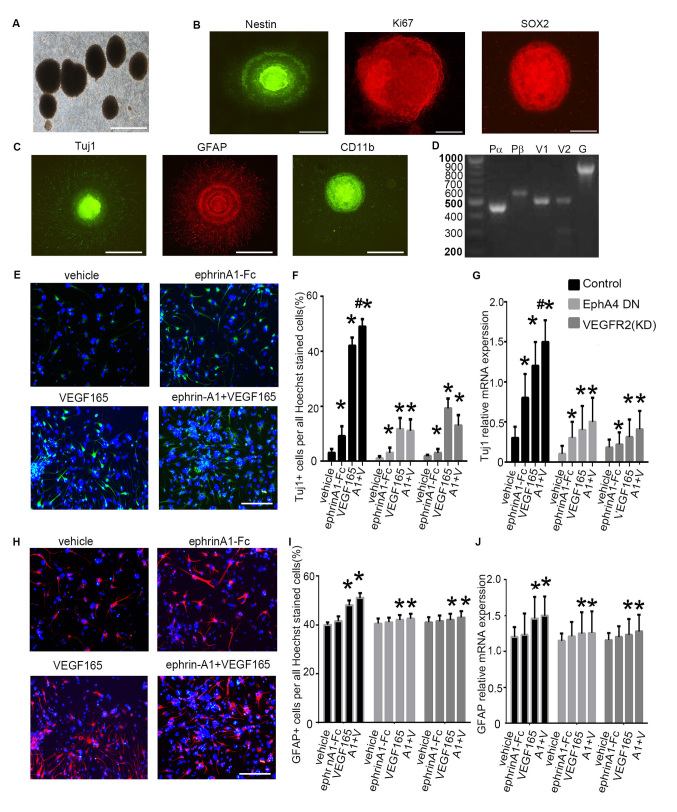
Figure 3.
Differentiation of mouse embryonic NSPCs under clustered ephrin-A1-Fc and/or VEGF165 stimulation. (A) Cultured NSPCs grew as neurospheres. (B) Immunofluorescence of the neurospheres show that the cells were nestin+, Ki67+ and SOX2+. (C) NSPCs differentiated into neurons (Tuj1+), astrocytes (GFAP+), and oligodendrocytes (CD11b+). Scale bars, 100 µm. (D) Expression of VEGFRs and PDGFRs in mouse embryonic NSPCs. Reverse transcription PCR was performed with equal amounts of total RNA isolated from mouse embryonic NSPCs. Fragment lengths are indicated on the left in base pairs. (E) NSPC differentiation was induced under ephrin-A1 stimulation. Tuj1+ cells in the different groups were stained after culturing for 7 days in normal medium or medium containing clustered ephrin-A1-Fc (0.5 µg/ml) and/or VEGF165 (20 ng/ml). (F) The proportion of Tuj1+ cells per all Hoechst-stained cells in the different treatment groups was analyzed. (G) The mRNA expression levels of Tuj1 in NSPCs cultured in normal medium or medium containing ephrin-A1 and/or VEGF165 was also examined. (H) GFAP+ cells in the different groups were stained after culturing for 7 days in normal medium or medium containing clustered ephrin-A1-Fc (0.5 µg/ml) and/or VEGF165 (20 ng/ml). (I) The proportion of GFAP+ cells and (J) mRNA expression levels of GFAP were calculated. NSPCs were transfected with dominant-negative EphA4 mutant or with kinase-negative VEGFR2 mutant prior to stimulation. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. For (F) and (I), n=3 in three separate experiments. For (G) and (J), n=5 in three separate experiments. *P<0.05 vs. the control group; #P<0.05 vs. VEGF165 treatment alone. DN, dominant negative; Eph, ephrin receptor; fc, fragment crystallizable region; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; NSPC, neural stem and progenitor cell; Pα, PDGFRα; Pβ, PDGFRβ; Tuj1, β-tubulin III; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, VEGF receptor; KD, kinase-dead. A1 + V, ephrin-A1-Fc + VEGF165 stimulation.