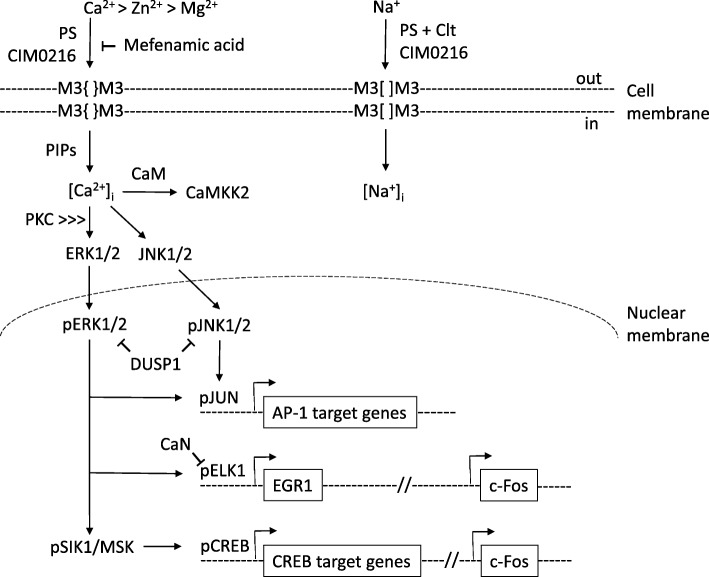
Fig. 4.
Schematic summary of TRPM3 channel gating and signal transduction. Agonists PS or CIM0216 stimulate Ca2+ influx via the canonical central pore (S5-P-S6) of TRPM3 homomeric tetramers ({}), whereas, mefenamic acid acts as an antagonist. Membrane phosphoinositides (PIPs) enhance PS-activated TRPM3 Ca2+ influx. PS in combination with Clt, or CIM0216 by itself, can also stimulate Na+ influx via an alternative pore opening ([]), distinct from the canonical TRP-pore. TRPM3 and TRPM1 monomers can also form heteromeric channels. TRPM3 channels are also permeable to Zn2+ and Mg2+, whereas, Zn2+ inhibits TRPM1 channels. TRPM3-elevated intracellular Ca2+ phospho-activates cytoplasmic MAPK signal transducers ERK1/2 and JNK1/2 that in turn phospho-activate nuclear transcription factors AP-1, ELK1, and CREB. Phosphatases CaN and DUSP1 provide feed-back inhibition of TRPM3-dependent Ca2+ signaling by de-phosphorylation of transcription factor pELK1 and the MAPKs pERK2 and pJNK1/2, respectively