Figure 6.
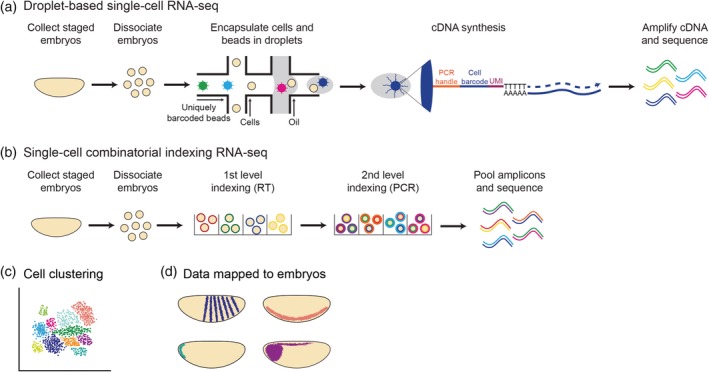
scRNA methodologies to build atlases of animal development. Single cell RNA‐sequencing (scRNA‐seq) methods used to generate atlases of animal development are illustrated using Drosophila as a model system. Staged embryos are collected and dissociated before being subjected to (a) droplet‐based scRNA‐seq or (b) single‐cell combinatorial indexing RNA‐seq (sciRNA‐seq). Droplet‐based scRNA‐seq methods utilize beads bearing primers that contain two unique barcodes, one that is cell‐specific and one that is transcript‐specific (Unique Molecular Identifier). The primers also contain a PCR handle for subsequent amplification. For sciRNA‐seq, cells are distributed to multiwell plates where they receive a well‐specific barcode during reverse transcription. Cells are then pooled and distributed to new multiwell plates where they receive a second well‐specific barcode during amplification. A third level of indexing can increase the number of cells processed in a single experiment (not shown). (c) Single‐cell transcriptomic data is represented as a t‐distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t‐SNE) or uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) plot, which cluster cells based on the similarity of their transcriptomes. (d) Cell type‐specific markers and in situ hybridization data can be used to map single‐cell transcriptomes back to a virtual embryo
