Figure 1.
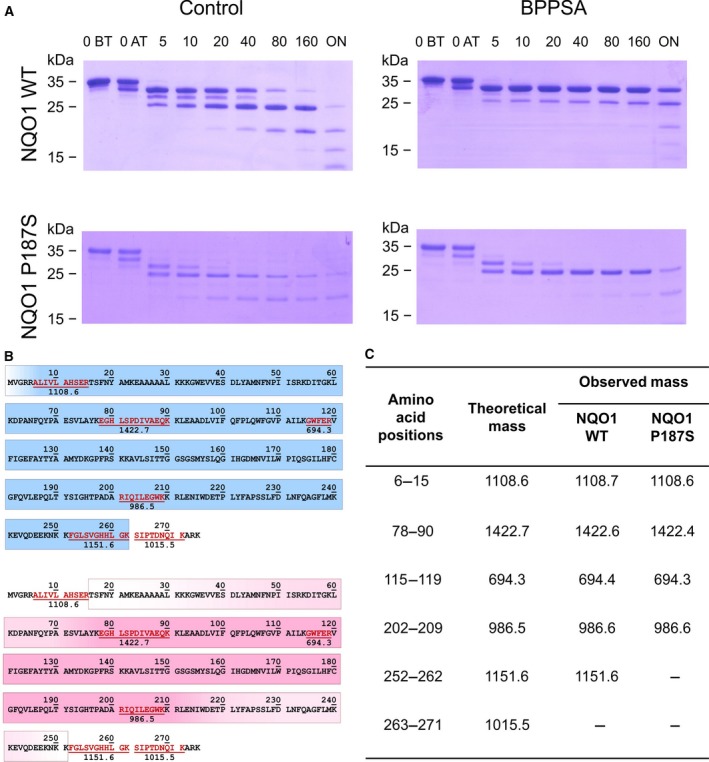
Limited trypsin proteolysis and MALDI‐TOF analysis of NQO1 WT and NQO1 P187S in the presence and absence of BPPSA. The compound stabilizes both the wild‐type and the P187S variant protein. (A) SDS/PAGE displaying the digestion over time for NQO1 WT and NQO1 P187S variant in the presence and absence of BPPSA. Lanes 1 and 2 show protein without trypsin (O BT) and protein taken out directly after addition of trypsin (O AT), lanes 3–8 show the digestion after 5–160 min, and the last lane shows the digestion overnight. (B) Theoretical fragments after trypsin digestion (displayed in red) were used to determine which part of NQO1 WT (blue) and NQO1 P187S variant (pink) was stabilized by the compound over time, and areas illustrated with a gradient could not be assigned due to too less information. (C) Peptides observed after MALDI‐TOF analysis of the stabilized SDS gel bands.
