Figure 2.
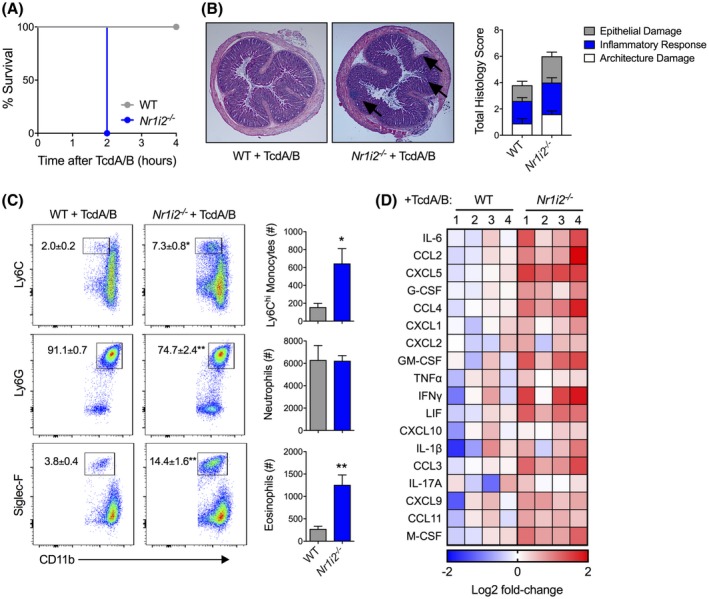
Deletion of Nr1i2 (pregnane X receptor; PXR) leads to increased susceptibility, and exacerbated tissue damage and inflammation following colonic exposure to TcdA/B. A, Survival curve of wild‐type (WT) and Nr1i2‐deficient (Nr1i2−/−) mice following intrarectal exposure to TcdA/B (n = 4 per group). B, Representative histological images and total damage scores of the colon from WT and Nr1i2−/− mice following 2 h of TcdA/B exposure. C, Representative flow cytometry plots and associated cell counts of infiltrating Ly6Chi monocytes (CD11b+Ly6C+), neutrophils (CD11b+Ly6G+), and eosinophils (CD11b+Siglec‐F+) in the colon following 2 h of TcdA/B exposure (n = 5 per group). The colon was also assessed for cytokine production, and the heatmap in panel D shows the top colonic cytokines that are differentially produced between WT and Nr1i2−/− mice following exposure to TcdA/B (Log2 fold change in Nr1i2−/− mice compared to WT mice). All data are expressed as SEM. One‐way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test, *P < .05, **P < .01
