Figure 5.
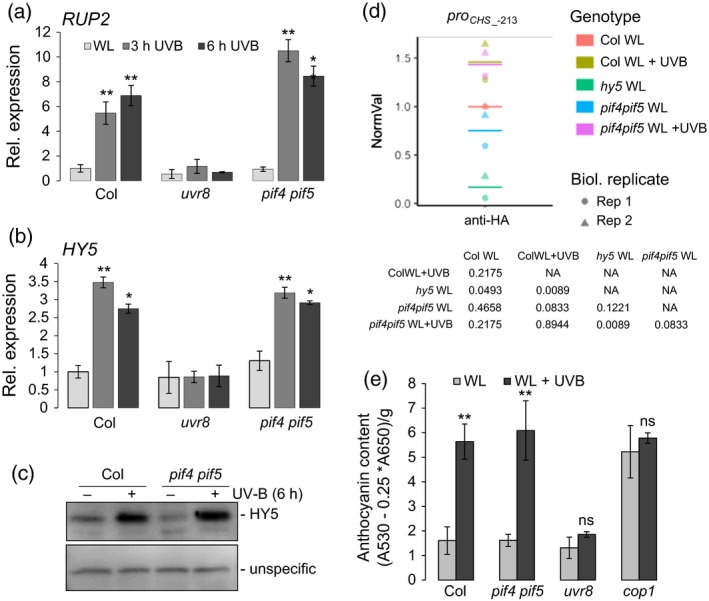
Induction of UV‐B‐inducible genes is independent of PIF4 and PIF5.
(a), (b) Quantitative real‐time PCR analysis of (a) RUP2 and (b) HY5 expression in 4‐day‐old wild‐type (Col), uvr8‐6 (uvr8) and pif4‐101 pif5‐3 (pif4pif5) seedlings exposed to narrowband UV‐B for 3 and 6 h (3 h/6 h UVB) or not (WL). Error bars represent the SE of three biological replicates. Asterisks indicate a significant increase in transcript abundance compared with that under WL (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). Error bars represent the SE of three biological replicates.
(c) Immunoblot analysis of HY5 levels in 4‐day‐old wild‐type (Col) and pif4‐101 pif5‐3 (pif4pif5) seedlings grown under white light (−) or white light supplemented with a final 6 h of UV‐B (+). An unspecific band is shown as a loading control.
(d) UV‐B‐responsive HY5 chromatin association in wild‐type plants (Col) was compared with that in the pif4 pif5 mutant, with that in hy5 plants being included as a negative control. Five‐day‐old seedlings were grown under white light and exposed to a final 6 h of narrowband UV‐B (+) or not (−). Chromatin immunoprecipitation‐qPCR was performed for the CHS promoter. The number of the analyzed DNA fragment (proCHS_‐213) indicates the position of the 5′ base pair of the amplicon relative to the translation start site (referred to as position +1). The percentage of DNA associated with HY5 relative to total input DNA of two independent biological replicates was normalized against the Col WL sample (NormVal, Col WL = 1). Means are represented as horizontal bars. P‐values from pairwise t‐tests using Holm's correction for multiple tests are shown.
(e) Anthocyanin accumulation in 4‐day‐old wild‐type (Col), pif4‐101 pif5‐3 (pif4pif5), uvr8‐6 (uvr8) and cop1‐4 (cop1) seedlings grown under white light either supplemented with narrowband UV‐B (WL + UVB) or not (WL). Error bars represent the SD of three biological replicates. Asterisks indicate a significant increase in anthocyanin levels under UV‐B compared with that under WL (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns, no significant difference).
