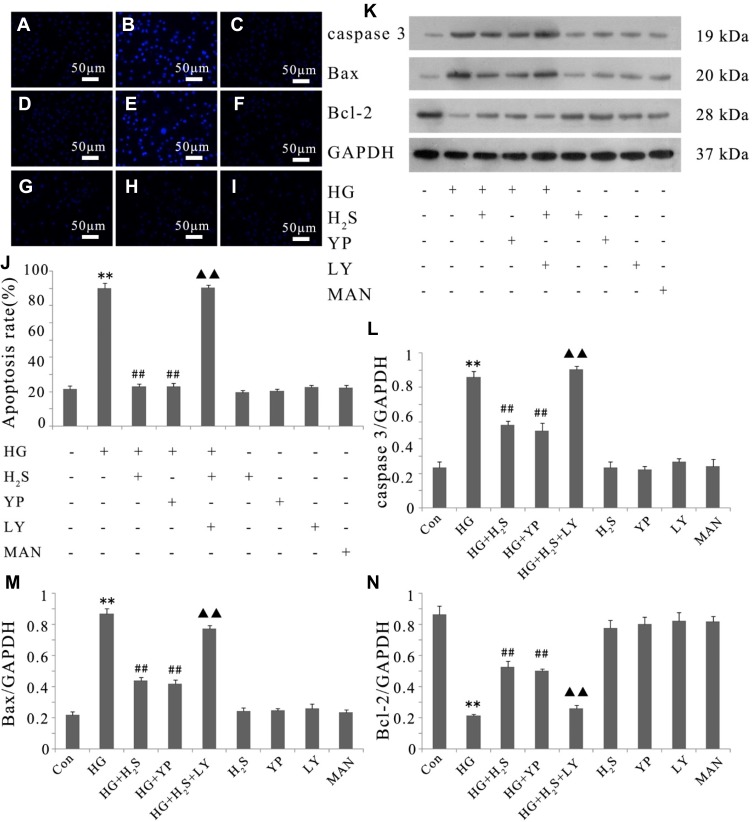
Figure 4.
Activation of PI3K/AKT/eNOS pathway is related to the protective effect of H2S against HG-induced apoptosis in HUVECs. (A–I) After the indicated treatments, HUVEC apoptosis was assessed by Hoechst 33258 staining followed by photofluorography. (A) Control group. (B) HUVECs were exposed to 33 mM glucose (HG concentration) for 24 hrs. (C) HUVECs were pretreated with 400 μM NaHS before HG treatment. (D) HUVECs were pretreated with 20 μM 740 Y-P before HG treatment. (E) HUVECs were co-treated with 10 μM LY294002 and 400 μM NaHS prior to HG treatment. (F) HUVECs were treated with 400 μM NaHS alone. (G) HUVECs were treated with 20 μM 740 Y-P alone. (H) HUVECs were treated with 10 μM LY294002 alone. (I) HUVECs were treated with 33 mM mannitol alone. (J) The apoptosis rate was analyzed by cell counting kit 8 assay and ImageJ 1.41o software. (K) Variations in the expression levels of active (cleaved) caspase 3, Bax and Bcl-2 in the indicated groups. (L–N) Densitometric analysis of the results in (K). Experiments were repeated three times. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. **p < 0.01 compared with the control group; ##p < 0.01 compared with the HG-treated group; ▲▲p < 0.01 compared with the group pretreated with NaHS before HG treatment. Con, control group; HG, high glucose (33 mM); YP, 740 Y-P; LY, LY294002; MAN, mannitol.