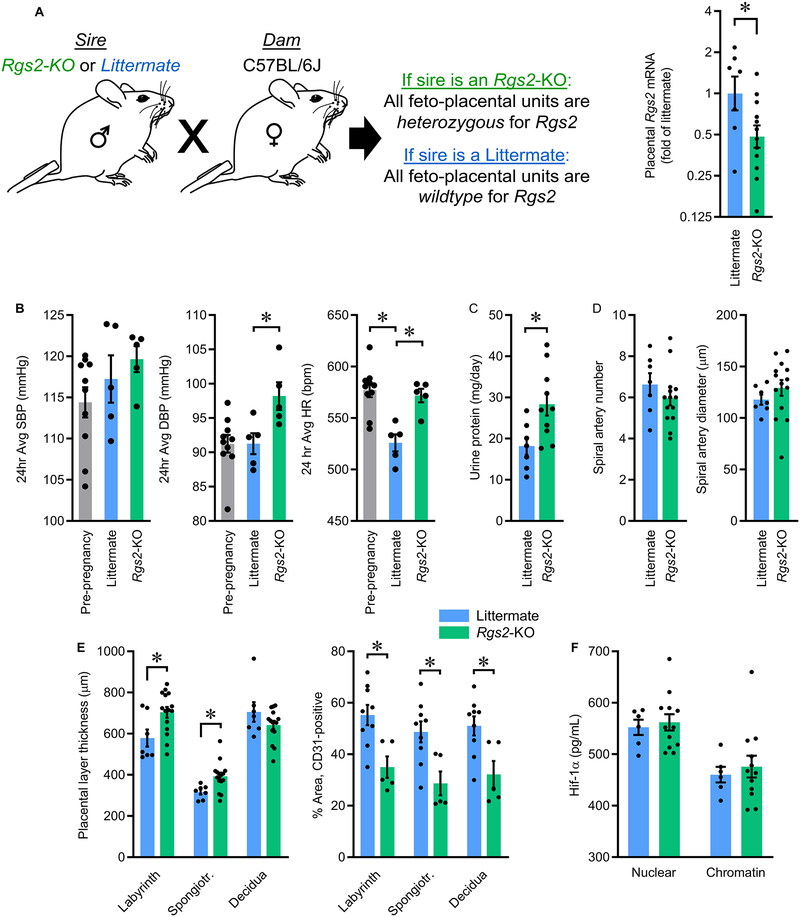
Figure 2. Selective breeding paradigm to reduce Rgs2 in the feto-placental unit of pregnant C57BL/6J mice.
(A) Schematic illustrating breeding scheme, and Rgs2 mRNA in GD17.5 placentas from dams mated with wildtype littermate (Littermate) or Rgs2-deficient (Rgs2-KO) males (Littermate n=7, Rgs2-KO n=12, each from an independent pregnancy). (B) Effects of reduced feto-placental Rgs2 on maternal systolic (SBP) and diastolic (DBP) blood pressure, and heart rate (HR) (Littermate n=5, Rgs2-KO n=5). (C) Maternal urine protein excretion (Littermate n=7, Rgs2-KO n=10). (D) Spiral artery number and diameter (Littermate n=7, Rgs2-KO n=14). (E) Thicknesses of placental layers, and percentage of area in placental layers staining positive for CD31 as an index of total vascularization (Littermate n=7, Rgs2-KO n=15). (F) Hif-1α localization in nuclear and chromatin-precipitated fractions of placentas at GD17.5 (Littermate n=6, Rgs2-KO n=12). Summary data presented as mean±SEM. *p<0.05 by two-tailed t-test (A, C), or Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons (B, E).