Figure 3.
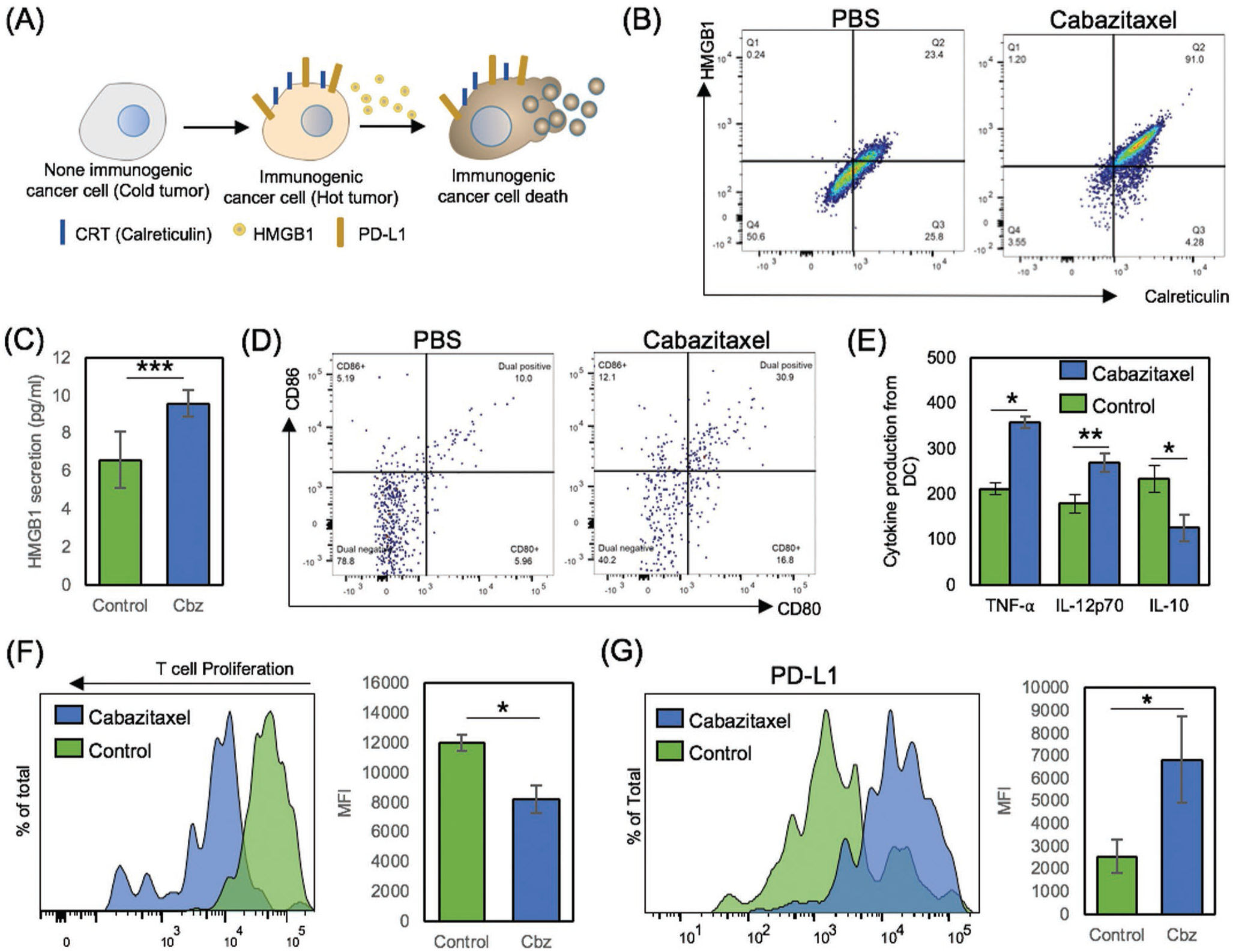
Immunogenic cell death induction (ICD) of Tramp C1 and followed adaptive immune responses with PD-L1 overexpression. A) Schematic illustration of ICD and following CRT, HMGB1, and PD-L1 expression. B,C) Validation of ICD after Cbz treatment. 1 × 106 Tramp C1 cells were cultured with 0.5 × 10−6 m of Cbz for 18 h. CRT and HMGB1, immunogenic cell death markers were analyzed by ELISA and flow cytometry. D) In vivo DC maturation test after Cbz treatment. Tramp C1 prostate tumor bearing mice were treated with PBS as negative control and Cbz only for ICD induction. Splenocytes were isolated and prepared with CD11c as DC marker, CD80, and CD86 as DC maturation marker. Data were obtained and analyzed from CD11c+ gate by flow cytometry. E) Production of TNF-α, IL-12p70 and IL-10 from ICD induced DCs after ex vivo restimulation. Cytokine profiles were determined by ELISA. F) Tumor specific T cell activation and proliferation. Tramp C1 cells were cultured with or without 0.5 × 10−6 m of Cbz for 24 h. Then, DCs were added to uptake ICD induced Tramp C1 cells. After 4 h, CMFDA labeled immunized T cells from donor mice were cocultured with primed DCs. After 5 d of cultivation, Tramp C1 specific T cell proliferation was observed and analyzed by flow cytometry. G) Cbz treatment dependent PD-L1 expression change was investigated after 18 h (PBS, 0.5 × 10−6 m of Cbz).
