Table 2:
Substrate scope of azetidine-2-carboxylates 4 obtained via palladium-catalyzed hydrogenation of donor–acceptor azetines 3.
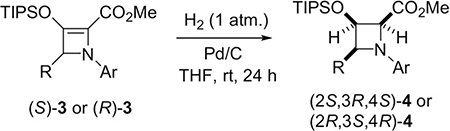 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry[a] | R | Ar | 4 | Yield [%][b] | dr[c] | ee [%][d] |
| 1 | H | C6H5 | 4 aa | 93 | N/A | racemic |
| 2 | Me | 3-F-C6H4 | 4 bc | 96 | > 20:1 | 90 |
| 3 | Et | C6H5 | 4 ca | 95 | > 20:1 | 85 |
| 4 | Et | 4-Cl-C6H4 | 4 cb | 92 | > 20:1 | 90 |
| 5 | Et | 3-Cl-C6H4 | 4 cd | 90 | > 20:1 | 91 |
| 6 | Et | 4-F-C6H4 | 4 cg | 92 | > 20:1 | 88 |
| 7 | Et | 3-F-C6H4 | 4 cc | 96 | > 20:1 | 92 |
| 8 | Et | 2-F-C6H4 | 4 ch | 97 | 7:1 | 88 |
| 9 | Et | 4-CF3-C6H4 | 4 ci | 96 | 10:1 | 91 |
| 10 | Et | 3-OMe-C6H4 | 4 cj | 94 | > 20:1 | 77 |
| 11 | Et | 3-Me-C6H4 | 4 ck | 95 | > 20:1 | 74 |
| 12 | Et | 4-Me-C6H4 | 4 cl | 97 | > 20:1 | 70 |
| 13 | Et | 4-Et-C6H4 | 4 cm | 93 | > 20:1 | 80 |
| 14 | octyl | 3-F-C6H4 | 4 dc | 95 | > 20:1 | 95 |
Reactions were carried out on a 0.25 mmol scale of azetine-2-carboxylate 3 in 4.0 mL of THF at room temperature with Pd on activated charcoal (2 wt. % of Pd metal) under H2 (1 atm) for 24 h.
Isolated yields after flash-chromatography are reported.
Determined from the 1H NMR spectra of purified compounds.
Enantiomeric excesses were determined using a Daicel Chiralpak AD-H and Chiralcel OD-H chiral columns.
