Figure 1. FMR1 GGG repeat length and gene expression.
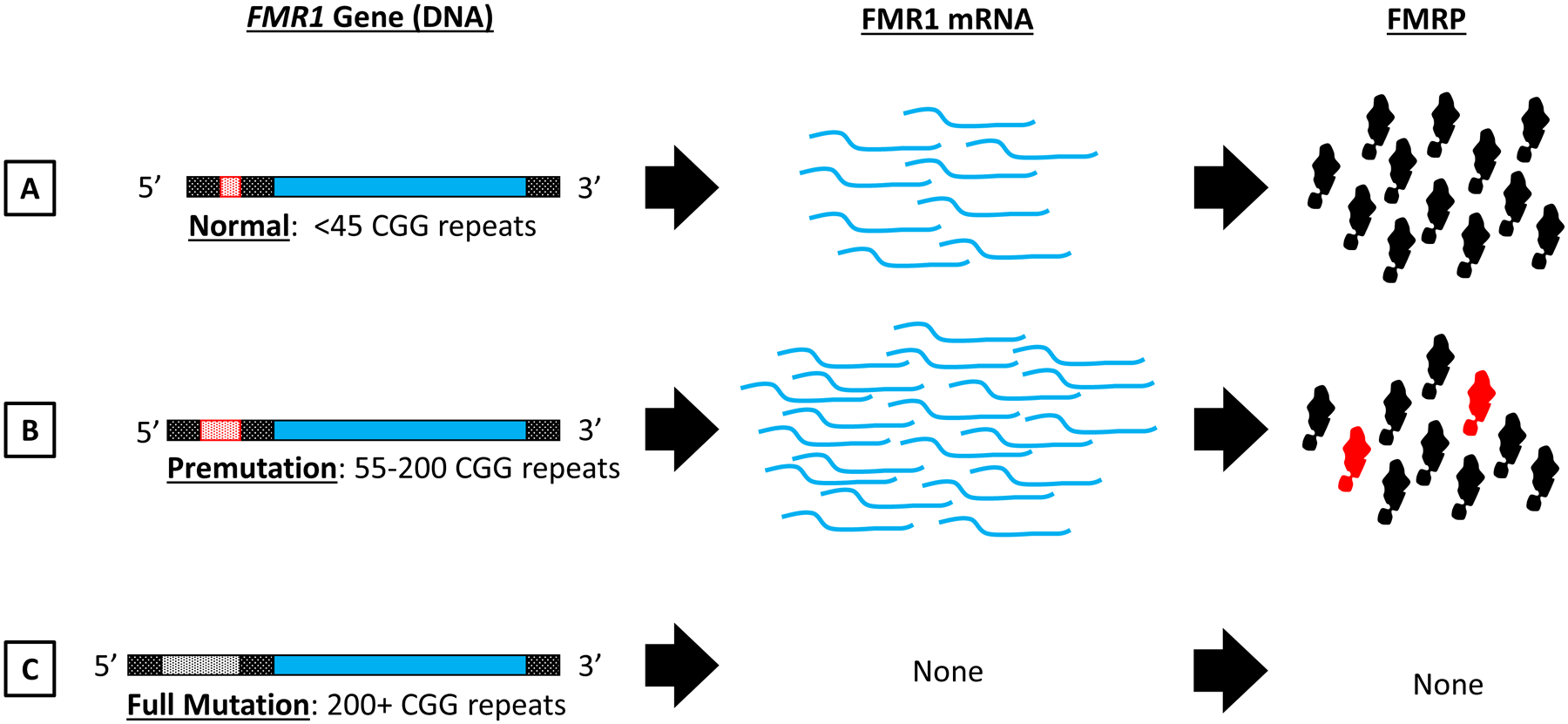
Overview of the relationship between CGG repeat length (A,B,C) within the FMR1 gene (left column) and its effects on FMR1 mRNA (middle) and FMRP protein synthesis (right). A) FMR1 alleles bearing less than 45 CGG repeats are considered in the normal range. B) CGG repeat expansion into the premutation range (containing 55–200 CGG repeats) causes an upregulation in FMR1 mRNA transcripts. For most premutation cases FMRP levels (black shapes) are not altered, although some individuals may show a modest reduction. Additionally, RAN translation of FMR1 mRNA produces toxic FMRpolyG protein species (red shapes). C) CGG repeat expansion into the full mutation range (200+ repeats) causes hypermethylation of the FMR1 gene, resulting in full transcriptional and translational silencing. Figure Key: FMR1 Gene: Open reading frame indicated with solid blue, non-coding 5’ and 3’ regions indicated with shaded black pattern. CGG repeat is located in the 5’ untranslated region (red shaded in A and B, white shaded in C to represent hypermethylation of the gene). FMR1 mRNA transcripts indicated with curved blue lines. FMRP protein represented as black shapes and FMRpolyG is represented as red shapes.
