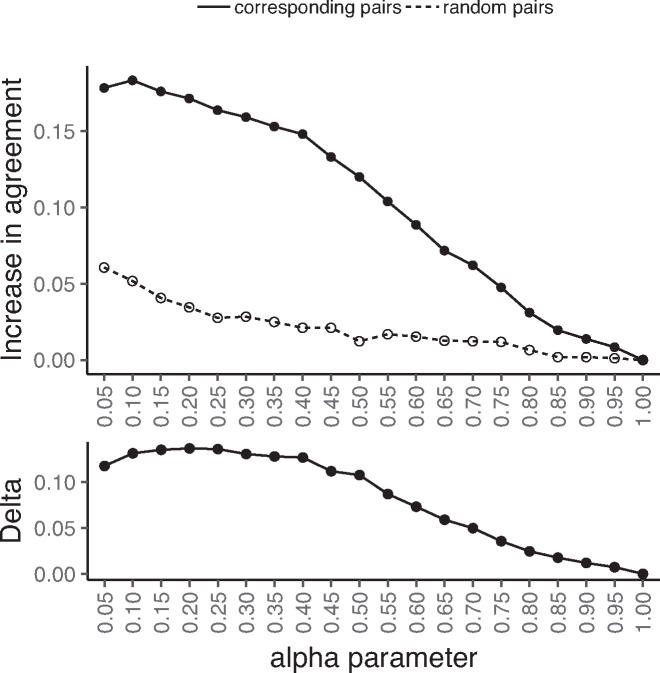
Figure 1.
Rewarding within-dataset consistency increases across-dataset agreement. For two independent datasets of single-domain C2H2-ZF specificities, we apply the QP formulation to each dataset separately for different values of α (x-axis; lower value implies more information sharing). (Top) For each α, for all proteins shared between the two datasets, we compare their jointly inferred specificities in each of the two datasets and compute the increase in the fraction of corresponding columns in agreement as compared to the agreement between the initial PWMs (solid line; y-axis). This increase is substantially larger than when randomly pairing PWMs across the two datasets (dashed line; y-axis). (Bottom) As a function of α, we consider the difference in the rate of across-dataset agreement increase for corresponding versus random core sequence pairings (solid line minus dashed line from top panel; y-axis), and observe a plateau around α = 0.4 where rates become similar.