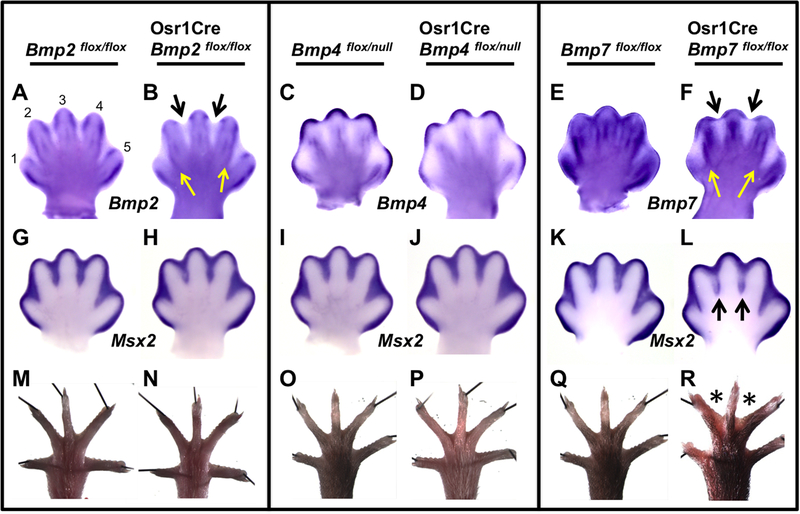
Fig. 1.
Limb ID-specific inactivation of Bmp7 results in a decrease of BMP signaling and soft-tissue syndactyly. (A–L) Whole-mount in situ hybridization (WISH) assays were performed using the riboprobe indicated on E13.5 hindlimbs of embryos of the specified genotype. (A–F) The indicated riboprobe is complementary to the region of DNA deleted by Cre and therefore can only detect the mRNA derived from the unrecombined allele. In Osr1Cre; Bmp2flox/flox (B) and Osr1Cre; Bmp7flox/flox (F) mutants, expression is absent in ID 2 and 3 (black arrows) except for a small region in the sub-AER mesenchyme. In ID 1 and 4 of these mutants, expression is mostly absent except along the ID/ digit border (yellow arrows). (G–L) Msx2 expression. A downregulation was observed only in ID 2 and 3 of Osr1Cre; Bmp7flox/flox mutants (L, black arrows). (M–R) Adult hindlimbs; black lines are pins holding samples in place. Syndactyly (asterisks) is observed in hindlimbs of Osr1Cre; Bmp7flox/flox mutants (R) but not in other genotypes. All views are dorsal with anterior to the left. Numbers 1 through 5 denote corresponding digits.