Figure 3.
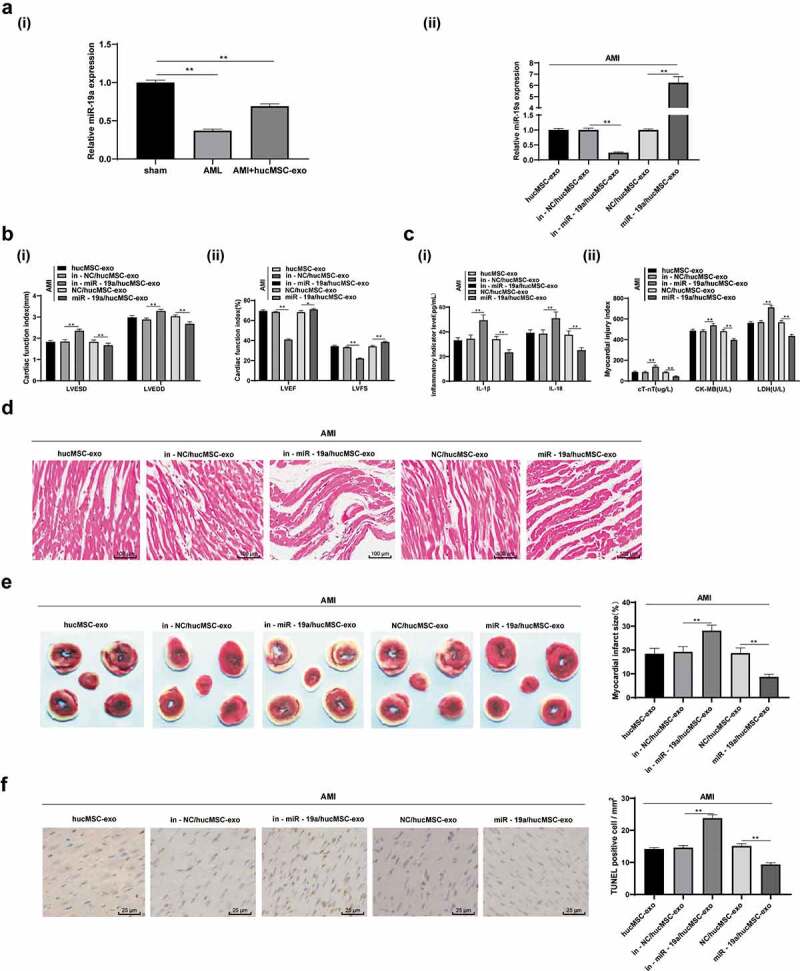
hucMSC-exo attenuates AMI injury in rats by releasing miR-19a. (a). Relative miR-19a expression in AMI tissues measured by RT-qPCR; (b). Relative LVESD, LVEDD, LVEF and LVFS measured by echocardiograph detection, n = 15; (c). Relative levels of IL-1β, IL-18, cT-Nt, CK-MB and LDH measured by ELISA, n = 15; (d). Representative images of histopathological changes of rat hearts detected by HE staining (n = 5); (e). The myocardial infarct size was measured by TTC staining (n = 5); (f). Apoptosis of rat heart tissues detected by TUNEL assay (n = 5). **p < 0.01. All experiments were repeated for three times. Data in panel A, E and F were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was used for pairwise comparison after ANOVA. Data in panel B and C were analyzed by two-way ANOVA, and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was used for pairwise comparison after ANOVA. hucMSC-exo, human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-exosome; miR-19a, microRNA-19a; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction; LVESD, left ventricular end systolic diameter; LVEDD, left ventricular end diastolic diameter; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; LVFS, left ventricular fractional shortening; IL, interleukin; cTnT, cardiac troponin T; CK-MB, creatine kinase isoenzyme MB; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HE, hematoxylin and eosin; TTC, 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick end labeling; ANOVA, analysis of variance.
