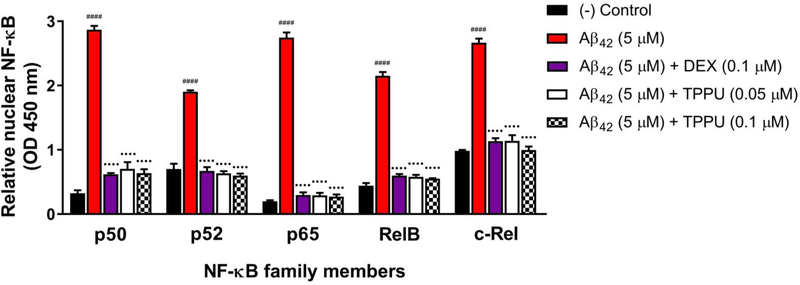
Figure 9.
TPPU suppressed activation and nuclear translocation of the transcription factor NF-κB in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. NF-κB family members (p50, p52, p65, RelB, and c-Rel) in the nuclear extracts were monitored with TransAM NF-κB assay. 5 μM Aβ42 treatment for 8 h significantly induced translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus. Pretreatment with various concentrations of TPPU (0.05 to 0.1 μM) or 0.1 μM DEX for 1 h followed by treatment of 5 μM Aβ42 for 8 h significantly reduced levels of all five NF-κB subunits in neuronal nuclei. Data were the mean of duplicate of six independent experiments with ± SEM (n = 6). Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. ####p < 0.0001 relative to vehicle control; ••••p < 0.0001 relative to the 5 μM Aβ42 treatment. Dexamethasone (DEX) known as the NF-κB/p38 MAPK inhibitor for anti-inflammatory activities was used as a reference control.