Figure 1:
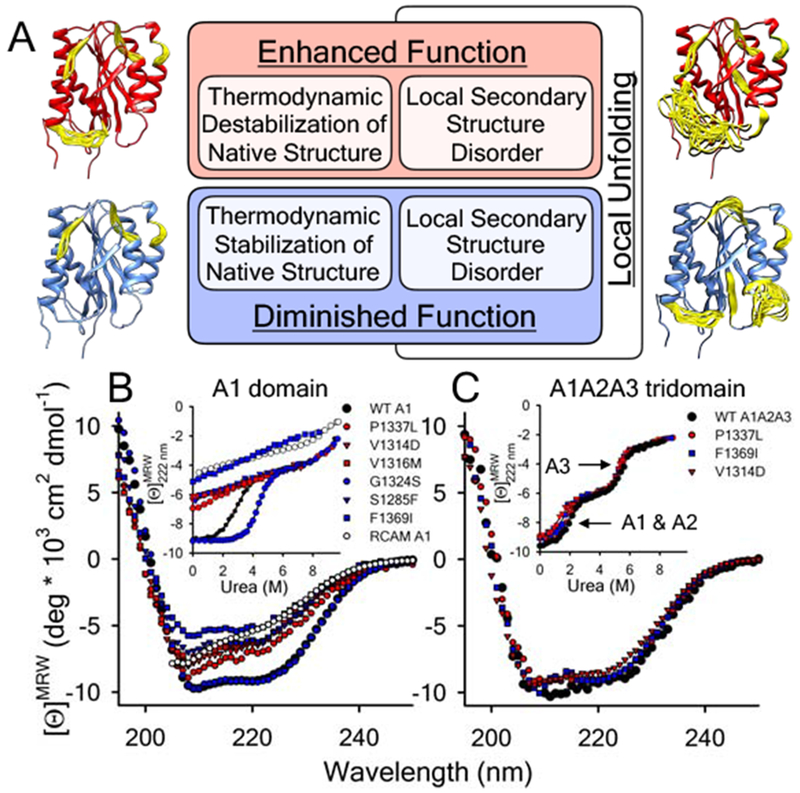
A) Proposed local secondary structure dynamics driven affinity regulation base on what is currently understood about how VWD mutations alter A1 domain structure and function [10–12,27,29–32,34]. Models of the A1 domain (PDB ID = 1AUQ [61]), generated with Mini-Protein MODelling (MPMOD) [62] and rendered using UCSF Chimera [63]. B & C) Far-UV CD spectra and urea denaturations (Insets) of the A1 (panel B) and A1A2A3 (panel C) VWD variants studied by LTMS and HXMS. B) wild-type A1 domain and VWD variants, P1337L, V1314D, V1316M, G1324S, S1285F, F1369I, and reduced A1. Inset: urea-induced unfolding of the proteins monitored at λ = 222nm. C) wild-type, P1337L, V1314D and F1369I A1A2A3 tridomains. Inset: urea-induced unfolding of the tridomains monitored at λ = 222nm. A1 and A2 domain unfolding precedes unfolding of the A3 domain (arrows). Black = wild-type, Red = type 2B VWD gain-of-function (GOF), Blue = type 2M VWD loss-of-function (LOF). Far-UV CD data for the A1 domain in panel B was originally published in [10].
