Figure 6:
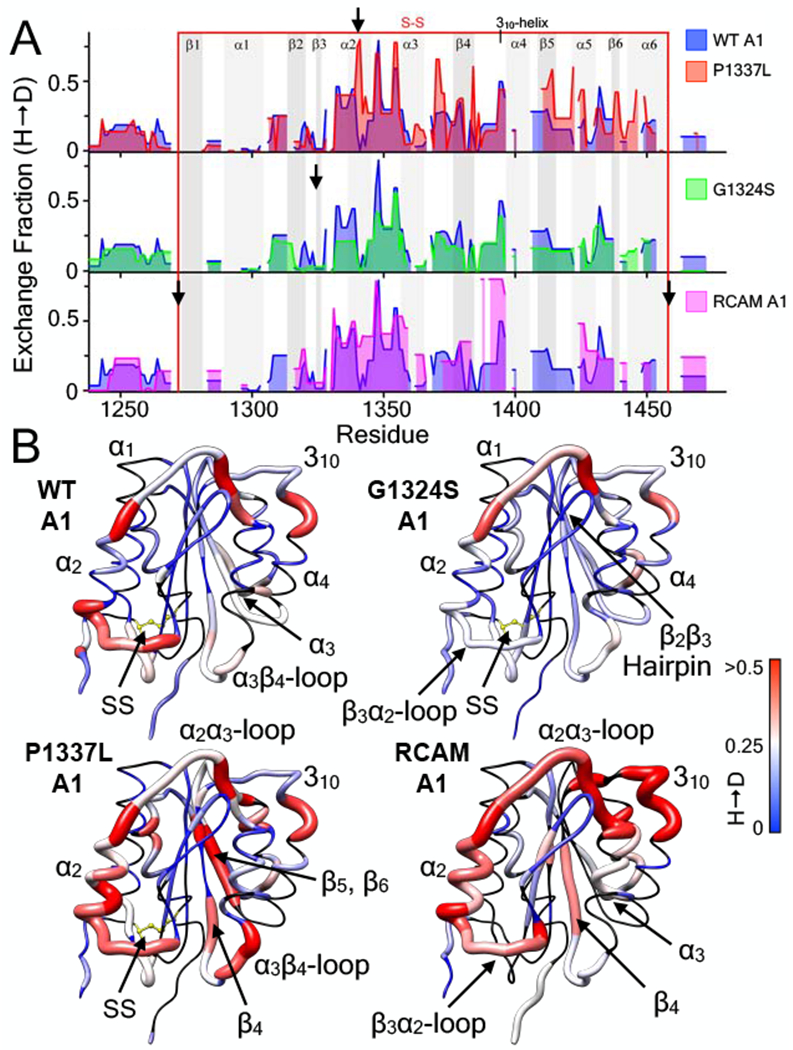
Effect of VWD mutations on the hydrogen deuterium exchange (H → D) of the A1 domain (E. coli). A) 1 hour hydrogen deuterium exchange (H → D) of wild-type A1 (all panels, blue area), P1337L A1 (type 2B GOF VWD, top panel, red area), G1324S A1 (type 2M LOF VWD, middle panel, green area), and RCAM A1 (type 2B GOF VWD where cysteines are reduced and carboxyamidated [11, 30], bottom panel, magenta area) as a function of residue position. HXMS of wild-type and RCAM A1 were previously performed in triplicate at 1, 5, 10, 20 and 30 minutes, 1, 3 and 6 hours, and overnight time points (see [11]). HXMS of P1337L A1 and G1324S A1 were performed in triplicate at 1 minute, 1 hour and overnight (HXMS Supporting Information). Heavy black arrows indicate the location of the mutation in the sequence. Gray vertical areas represent the indicated secondary structure elements (top). Red vertical lines represent the disulfide bond. B) HX fraction mapped onto the structure of the A1 domain (pdb ID = 1AUQ [61]). Black = not resolved, blue = 0, white = 0.25, red ≥ 0.5. All structures are rendered using UCSF Chimera [63].
