Figure 4.
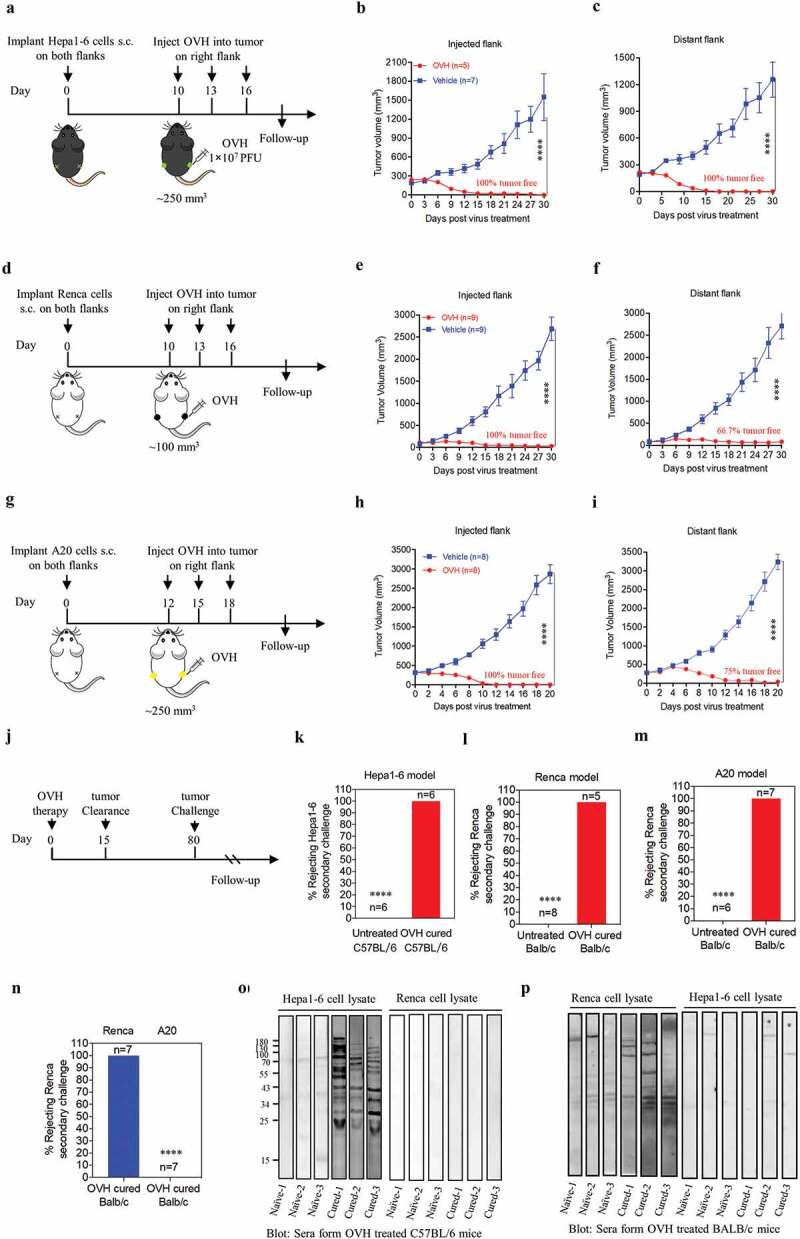
OVH therapy can eradicate local and distant tumors in the immunogenic tumor models. (A, D, G) Timeline of treatment in C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice. Mice were s.c. inoculated with Hepa1-6 (A), Renca (D) or A20 cells (G) in both flanks, and treated 10 or 12 days later with OVH or vehicle. (B) Tumor growth of virus-injected (right flank) Hepa1-6 tumors. (C) Growth of distant (left flank) Hepa1-6 tumors. (E) Tumor growth of virus-injected Renca tumors. (F) Tumor growth of distant Renca tumors. (H) Tumor growth of virus-injected A20 tumors. (I) Tumor growth of distant A20 tumors. (J-M) The subset of cured long-term survivors from the Hepa1-6 model (K), Renca model (l), and A20 model (M) groups, together with naïve mice, were re-challenged with 1 × 107 of the corresponding tumor cells. The percentage of long-term survivors that rejected the secondary challenge was calculated. (N) A subset of cured long-term survivors from the Renca model and A20 model groups were re-challenged with 1 × 107 Renca tumor cells. The percentage of long-term survivors that rejected secondary challenge was calculated. (O) Western blot analysis of Hepa1-6 cell lysate and Renca cell lysate with serum from OVH-treated C57BL/6 mice bearing Hepa1-6 tumors or naïve mice. (P) Western blot analysis of Hepa1-6 cell lysate and Renca cell lysate with serum from OVH-treated BALB/c mice bearing Renca tumors or naïve mice. The number of mice (N) used in the experiments is shown in individual figures. All values are presented as the mean ± SEM. **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001 by repeated measure ANOVA for B, C, E, F, H, I or unpaired two-tailed Student’s t tests for K-N.
