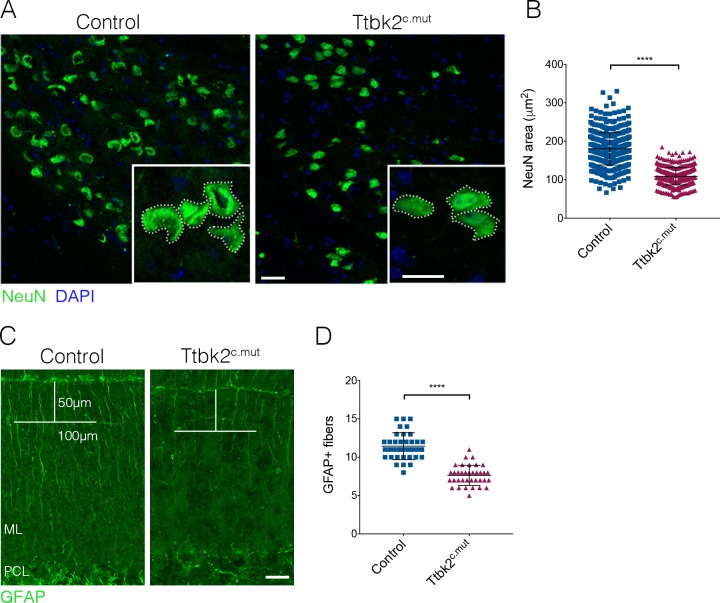
Figure 2. ION and glial cells are affected by loss of Ttbk2.
(A) Representative images of neurons in the inferior olivary nucleus (ION) located in the medulla. Neural somata are immunostained with NeuN (green). Insets show how the area was measured. Scale bar = 50 μm (20 μm inset). (B) Quantification of NeuN area. ION neurons have reduced area in Ttbk2c.mut animals compared to Control (each point represents a single cell measurement of which > 150 measurements were made per animal. n = 3 animals, p<0.0001 by unpaired student’s t-test, error bars indicate SEM). (C) Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) staining showing BG fibers throughout the molecular layer. In Ttbk2c.mut animals, density of these fibers is reduced. Quantification was made as previously described (Furrer et al., 2011), in which a 50 μm line was drawn from the pial surface of the folia, and a 100 μm line across. Glial fibers that fully crossed the 100 μm line were scored. Scale bar = 20 μm. (D) Quantification of GFAP+ glial fibers that crossed the 100 μm line (each point represents an image quantified, 36 images quantified per genotype across n = 3 animals. p<0.0001 by unpaired student’s t-test, error bars indicate SEM).