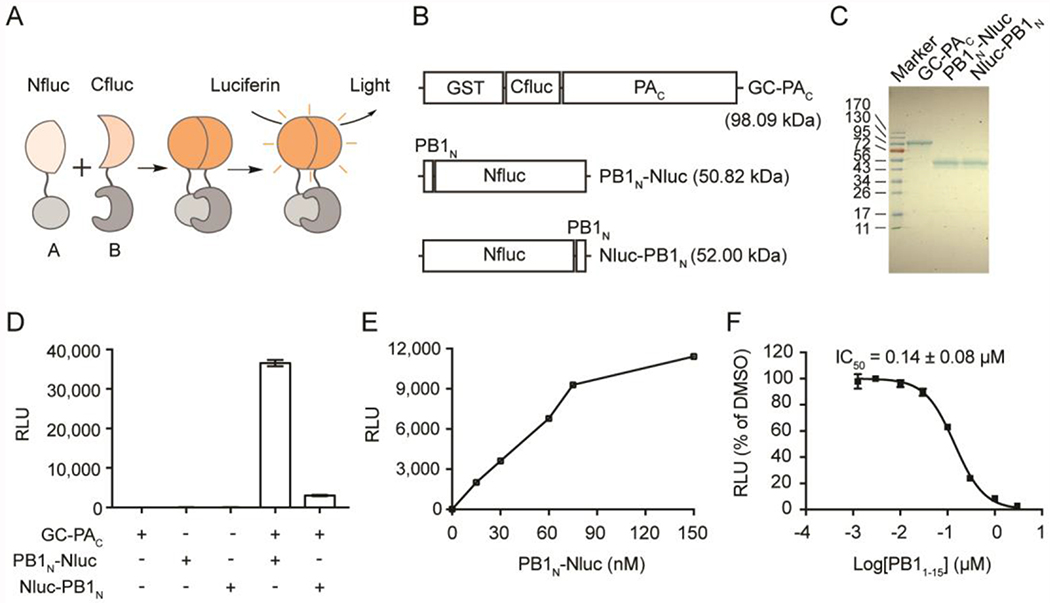
Figure 2. The in vitro PA-PB1 SLC assay.
(A) Cartoon representation of the assay principle for SLC assay. (B) The influenza PAC/PN1BN SLC constructs. GST-Cfluc (aa 398-550)-PAC aa 239-716 (named as GC-PAC), PB1N (aa 1-25)-Nfluc (aa 2-415) (named as PB1N-Nluc), and Nfluc (aa 2-415)- PB1N (aa 1-25) (named as Nluc-PB1N). (C) SDS-PAGE gel showing purified GC-PAC, PB1N-Nluc and Nluc-PB1N. (D) The positions of Nluc and Cluc affect luciferase activity. Equal concentrations (100 nM) of each pair of PAC-PB1N constructs were mixed (or alone) and incubated with luciferin substrate. (E) Dose-response of GC-PAC/PB1N-Nluc pair. GC-PAC at 60 nM was included in each experiment. Concentration of PB1N-Nluc was varied as indicated. (F) The influenza PB1 aa 1-15 peptide, PB11-15, inhibited the SLC in a dose-dependent manner. In all graphs, means and SD from triplicate experimental data were shown.