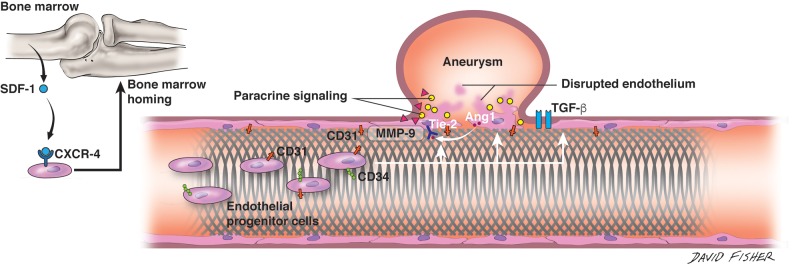
Fig 2.
Endothelialization along the flow-diverting stent. Interplay among the flow-diverting stent, native vessel endothelium, molecular factors at aneurysm dome, and circulating endothelial progenitor cells is depicted in cartoon format. Stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) released from the bone marrow binds to the C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR-4) receptor on circulating EPCs and directs homing of these cells to the bone marrow. At the site of flow-diverter placement, circulating EPCs (shown as CD31+ CD34+) are seen along device struts. At the aneurysm dome, several molecules, including matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), act to stimulate vascular repair. Ang-1 is furthermore released from the disrupted endothelium, where its prorepair action is mediated by the Tie2 receptor expressed on the vascular endothelium. TGF-β indicates transforming growth factor β. Artist: David Fisher, Dept of Neurosurgery, University of Alabama-Birmingham. Published with permission.